Based on Einstein's local realism and hidden variable model, Bell proposed the famous Bell inequality,
[1] which is an important resource in the quantum information theory. Chain inequality is an important kind of Bell inequality, which has $n$ ($n\geq2$) measurement bases, and the Clauser-Horne-Shimony-Holt (universally known as CHSH inequality
[2]) inequality can be assumed to be a special Chain inequality with $n=2$. More precisely, Chain inequality can be applied to propose device independent quantum information protocols,
[3-4] where security of the protocols can be guaranteed by the Chain inequality violation, not based on the perfect quantum states preparation and measurement assumption. More recently, Colbeck et al.
[5-10] have proved that the imperfect randomness could be amplified via Chain inequality.
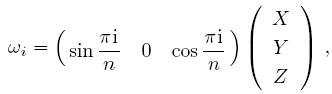
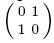 , $Y=\sigma_{y}=$
, $Y=\sigma_{y}=$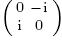 , and $Z=\sigma_{z}=$
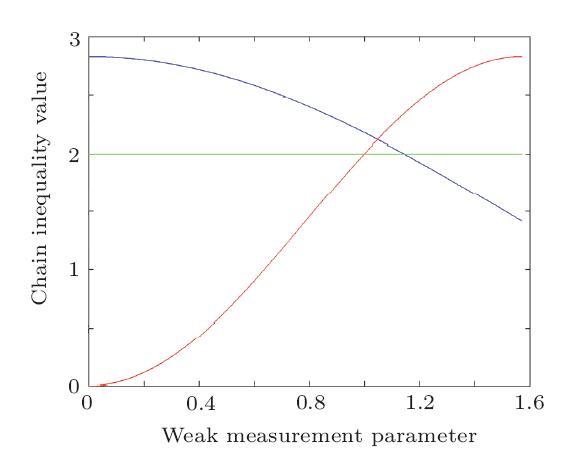
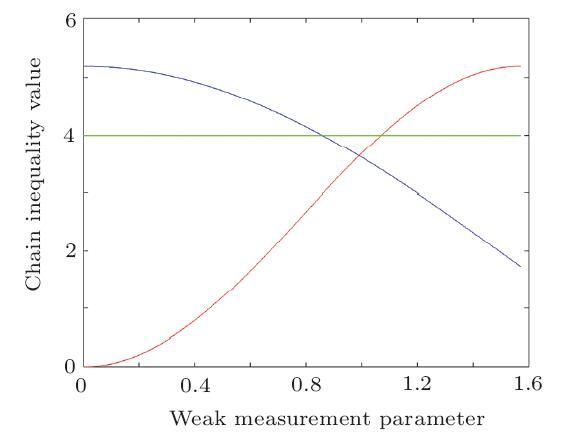
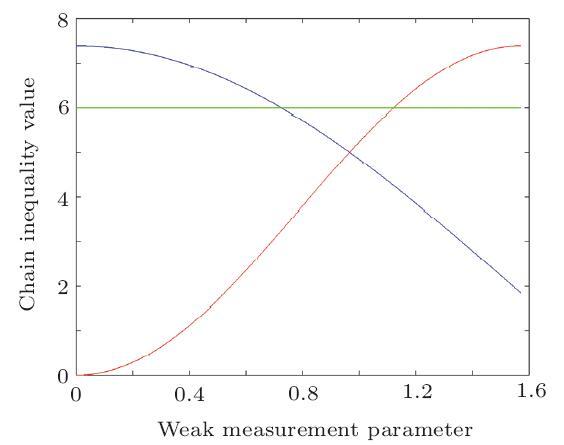
, and $Z=\sigma_{z}=$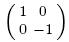 are Pauli operators. Specifically, if there are only four measurement bases (i.e. $N=2n=4$), Chain inequality is equal to the CHSH inequality.
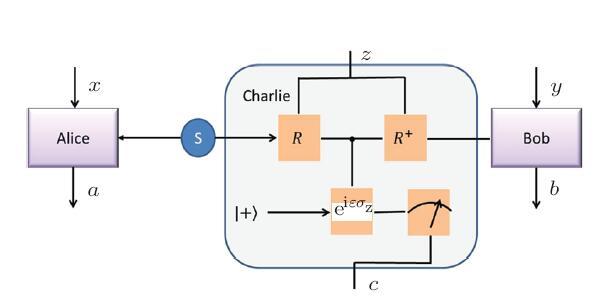
are Pauli operators. Specifically, if there are only four measurement bases (i.e. $N=2n=4$), Chain inequality is equal to the CHSH inequality. , where $\varepsilon$ is the weak measurement parameter. This process is equal to the operation that carries out collective measurement on the particle sent to Bob and Charlie's state $|+\rangle$, then Alice, Bob, and Charlie measure their quantum states to get the measurement outcomes. By considering Alice, Bob and Charlie as an integer system, the previous $R$ operation can be represented as
, where $\varepsilon$ is the weak measurement parameter. This process is equal to the operation that carries out collective measurement on the particle sent to Bob and Charlie's state $|+\rangle$, then Alice, Bob, and Charlie measure their quantum states to get the measurement outcomes. By considering Alice, Bob and Charlie as an integer system, the previous $R$ operation can be represented as