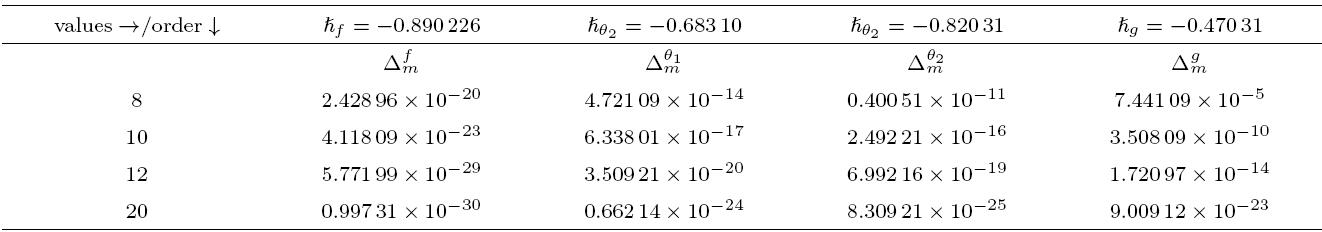
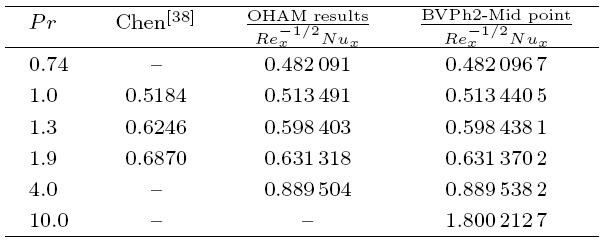
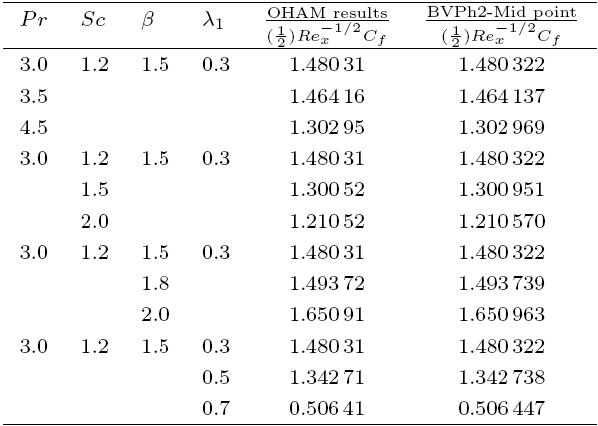
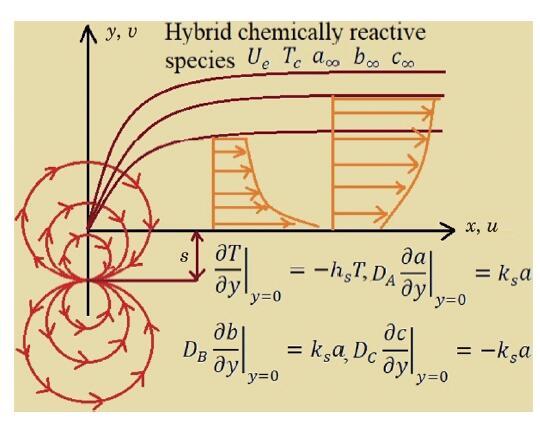
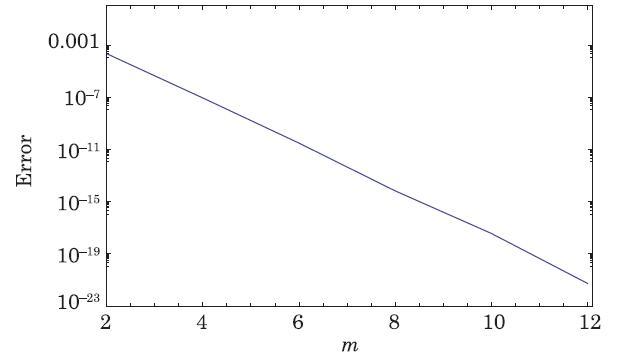
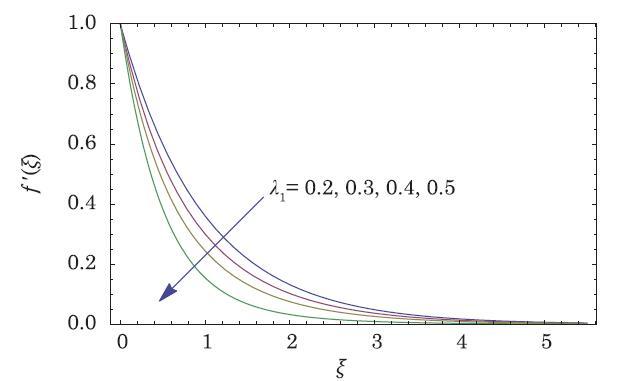
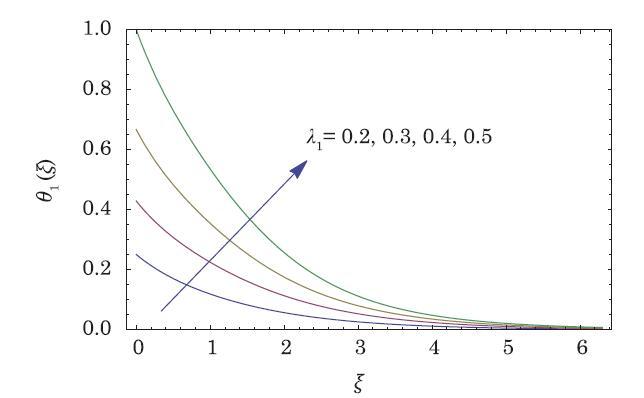
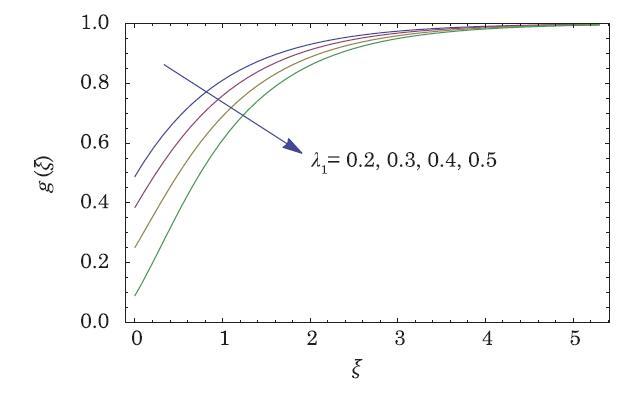
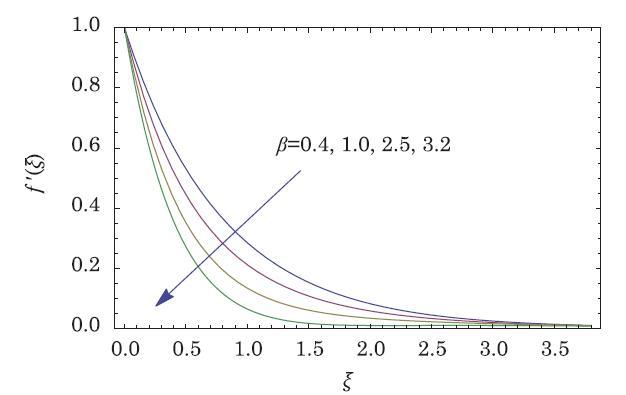
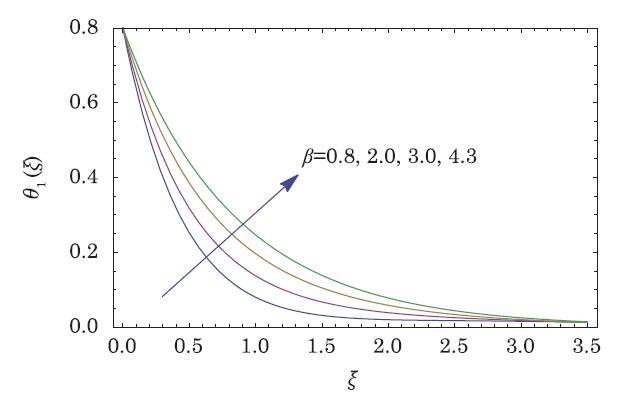
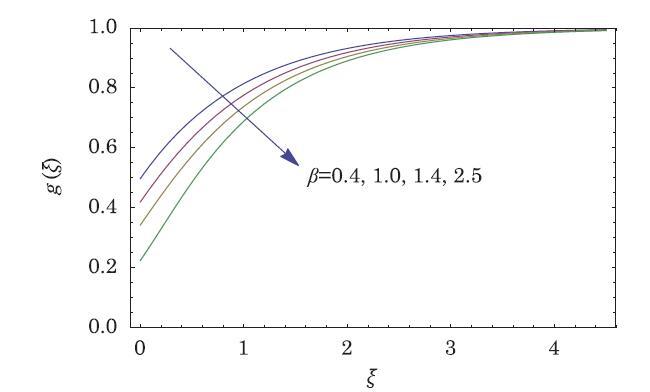
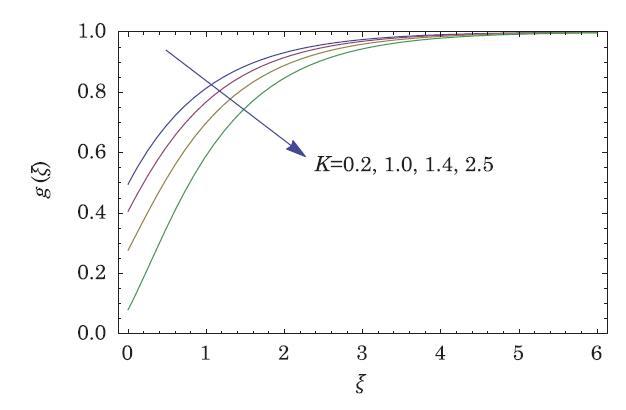
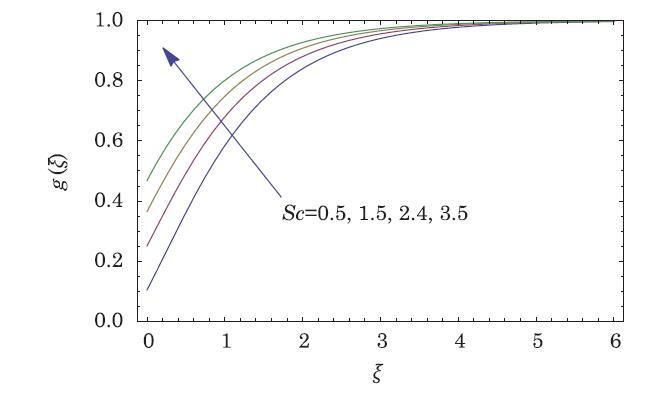
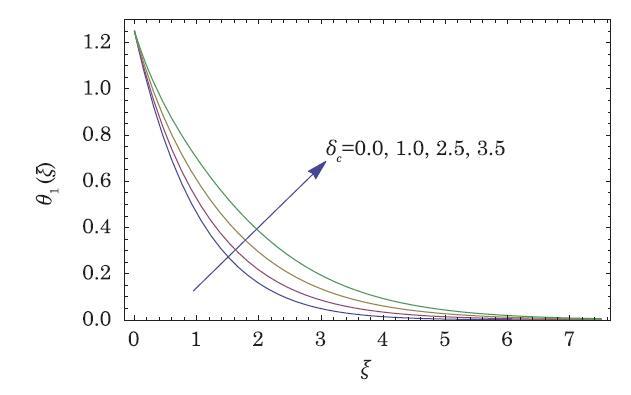
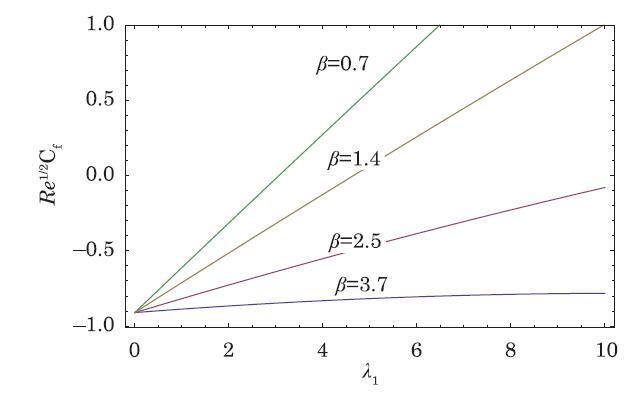
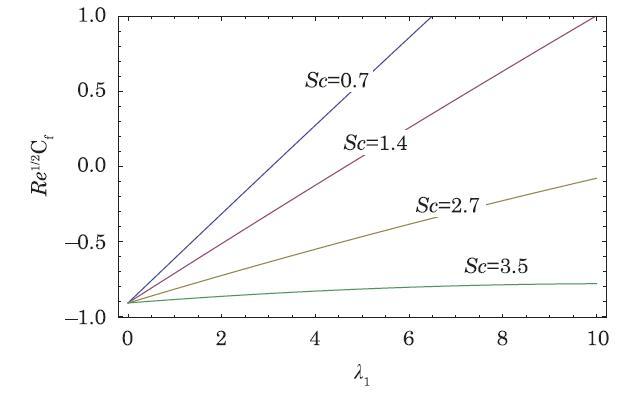
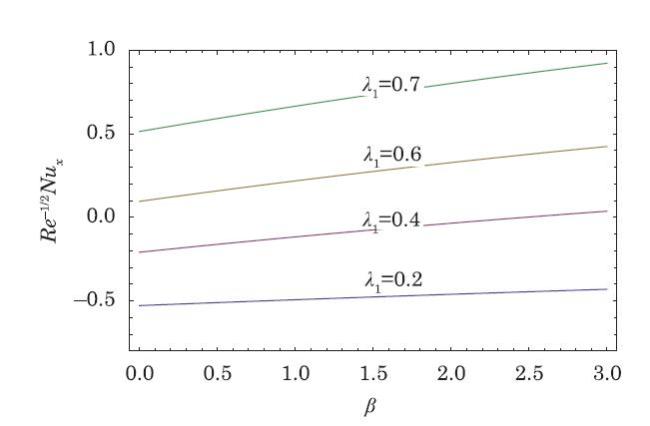
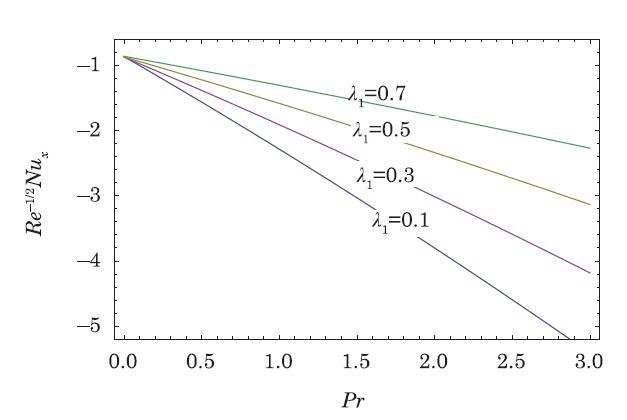
The packed bed tabular reactions of cooled or heated walls are usually employed in industry to accomplish heterogeneous or homogeneous catalytic reactions, which can be endothermic or exothermic. In gas-solid transport-reaction mechanisms, reaction take place within the solid phase, within liquid phase, or at liquid interface. Reaction between atoms/molecules of sundry coefficients can take place during their collision and or a third distinct atom/molecule may be sufficient for a reaction to occur. Several chemical reactions proceed very slowly, on not at all, except in the presence of a catalyst. A survey of the chemical aspects of heterogeneous, or surface reactions have been characterized by Scott,
[1] and Gray and Scott.
[2] A full talk of catalysis and a description of several of its practical applications is discussed in Refs. [
3-
5]. A heterogeneous mixture includes of either or both of (i) hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials in a unique mixture, or (ii) sundry conditions of matter; hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials would be a mixture of silicone grease, octane, and water. Fluids, solids, heterogeneous, and gasses might be made homogeneous by mixing, melting, or by permitting time to go for diffusion to appropriate the atoms/molecules equitably. For instance, mixing dye to water will make a heterogeneous solution, however, later on it reduced to a homogeneous. Homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions are important in several chemically reacting procedures. Homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions are important in several chemically reacting procedures. Merkin
[6] initiated the chemically reactive species in the flow induced by stretching sheet. The friction drag in a chemically reactive species was scrutinized by Chaudhary and Merkin.
[7] Bachok et al.
[8] characterized the effects of homogeneous$-$heterogeneous reactions in liquid flow. Kameswaran et al.
[9] expressed heat transfer in a chemically reactive species in the flow of a nanofluid. Khan and Pop
[10] characterized the two-dimensional flow of a chemically reactive species in the presence of stagnation point.