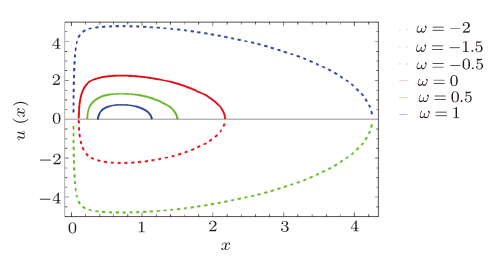
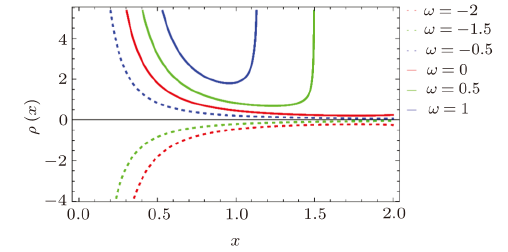
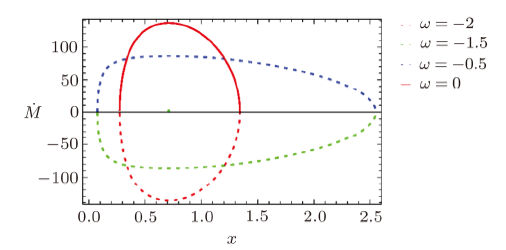
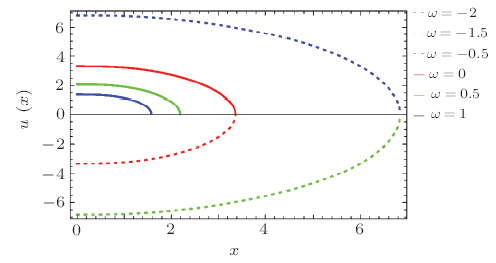
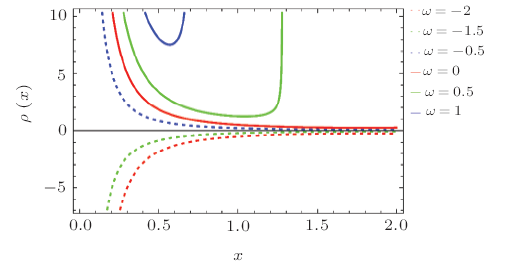
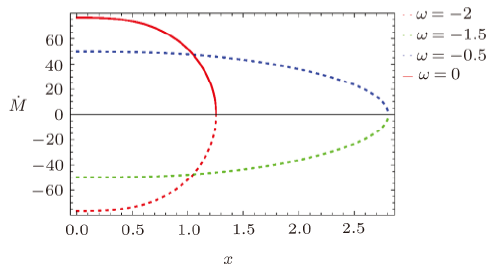
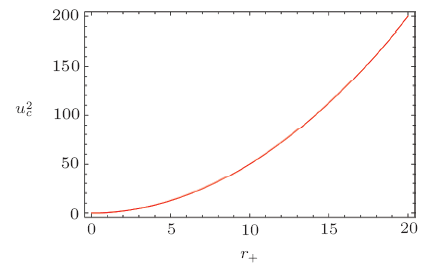
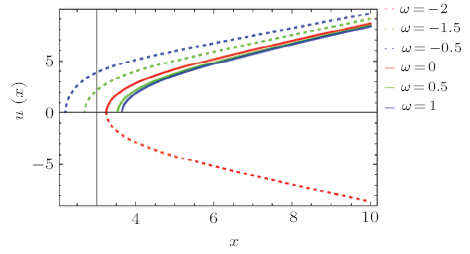
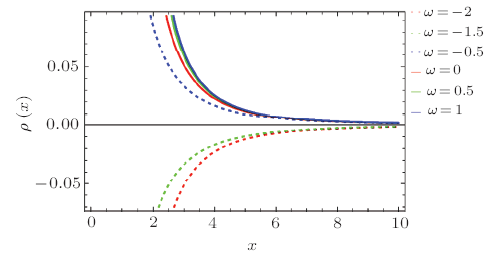
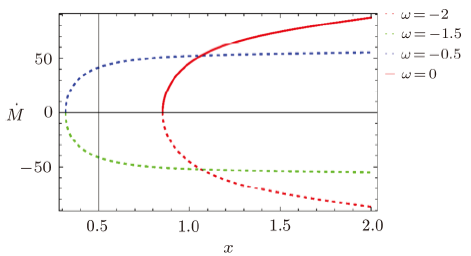
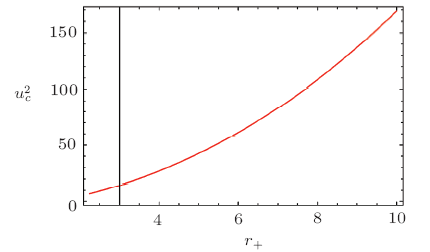
In the solution of Einstein field equations, presence of essential singularities in different BHs is a prime issue in general relativity.
[21] In order to solve this issue regular BHs (RBHs) have been constructed. The metrics of these BHs have no essential singularity hence are regular everywhere.
[22] Some of the RBHs satisfy weak energy conditions
[23] while strong energy conditions fails to hold. The necessary conditions for RBHs is to satisfy the weak energy conditions having de sitter center.
[24] RBHs have an important role to understand gravitational collapse. Bardeen
[25] introduced the first RBH known as Bardeen BH, and WEC hold for it. By utilizing Newtonian gravity Bondi
[26] studied accretion for some important compact objects. After the discovery of general relativity, the first person who discuss the accretion process for the Schwarzschild BH was Michel.
[27] Generalizing the work of Babichev et al., Debnath
[28] studied static accretion onto general static spherically symmetric BH. Bahamonde1 and Jamil
[29] studied more general ansatz for a static spherically symmetric spacetime. Jawad and Umair
[30] studied accretion onto well known BHs. Kim et al.
[31] worked on the accretion on static BH and Kerr-Newman BH of DE. Sharif and Abbas
[32] contributed their work for accretion on stringy charged BHs due to phantom energy.