Nowadays, microfluidic device applications are increasing in the fields of chemical separation, medical diagnostics, material synthesis, energy harvesting, and others.
[1-4] Normally, surface tension, pressure gradient, surface acoustic wave, electric field, magnetic field and their suitable combination have been implemented to manipulate microfluidic flow.
[5-8] Electroosmotic flow (EOF), defined as the motion of fluids in narrow confinements under the action of an axial electric field in the presence of an electric double layer (EDL) near the walls, has wide spectrum of applications.
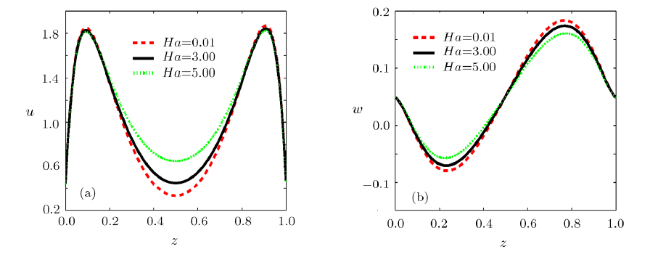
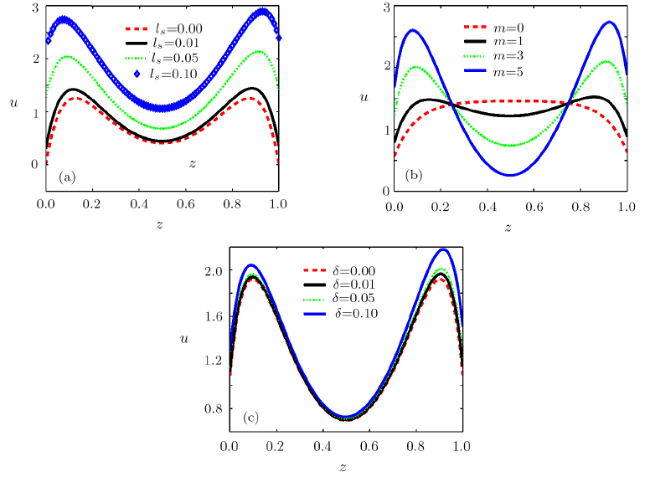
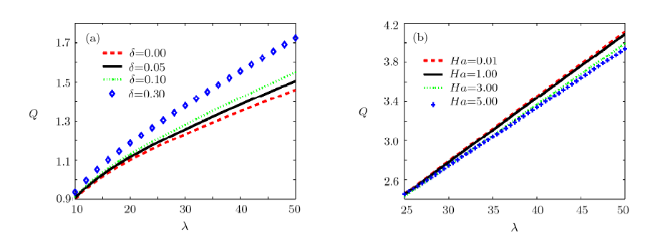
[9-11] In order to minimize the Joule heating effects in EOF, magnetodydrodynamic (MHD) micropump has been proposed. MHD flow is driven by Lorentz force generated by imposing a lateral electric field and a vertical magnetic field.
[12] Over recent years, many researchers have investigated the MHD flow in microchannel. Rivero and Cuevas
[13] considered the influence of slip condition on the MHD flow in a rectangular microchannel. Jian et al.
[14] analytically studied the transient rotating MHD flow for both DC and AC electric fields through a parallel microchannel. Si and Jian
[15] studied MHD flow of non-Newtonian fluids through two corrugated walls. In order to obtain augmented flow rates, the more general requirement of studying the interaction between EOF and MHD flow is needed. MHD EOF is produced by combining the Lorentz force and electric force in axial direction. Chakraborty and Paul
[16] analyzed the MHD EOF in narrow microchannels and obtained optimized flow rates. Driven by combination of electroosmotic, pressure and magnetic forces, unsteady MHD EOF of incompressible viscous fluid through a circular tube was developed with the Caputo Fabrizio time fractional derivative by Abdulhameed et al.
[17] Chakraborty et al.
[18] analyzed thermal behavior of MHD EOF in narrow channels taking viscous dissipation and Joule heating into account under constant wall heat flux. Abdulhameed et al.
[19] investigated the MHD EOF flow acted by an arbitrary time-dependent pressure gradient, electric field force and Lorentz force and heat transfer through a cylindrical microchannel. Jian
[20] investigated heat transfer and entropy generation of MHD EOF flow through a slit microchannel. Xie and Jian
[21] studied entropy generation of two-layer MHD EOF flow through microparallel channels. Sarkar et al.
[22] studied heat transfer of MHD EOF with interfacial slip.