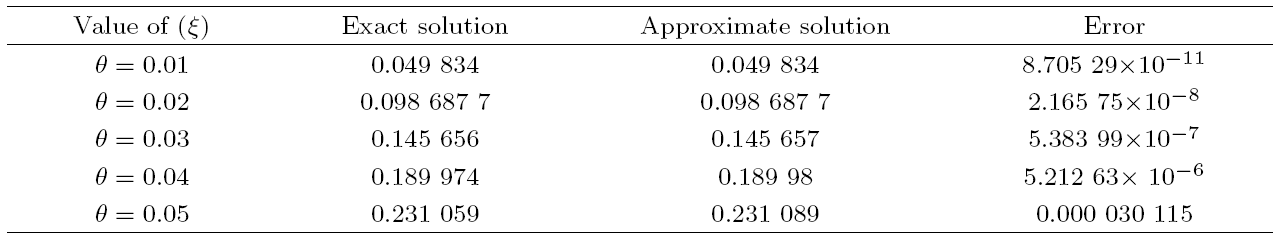
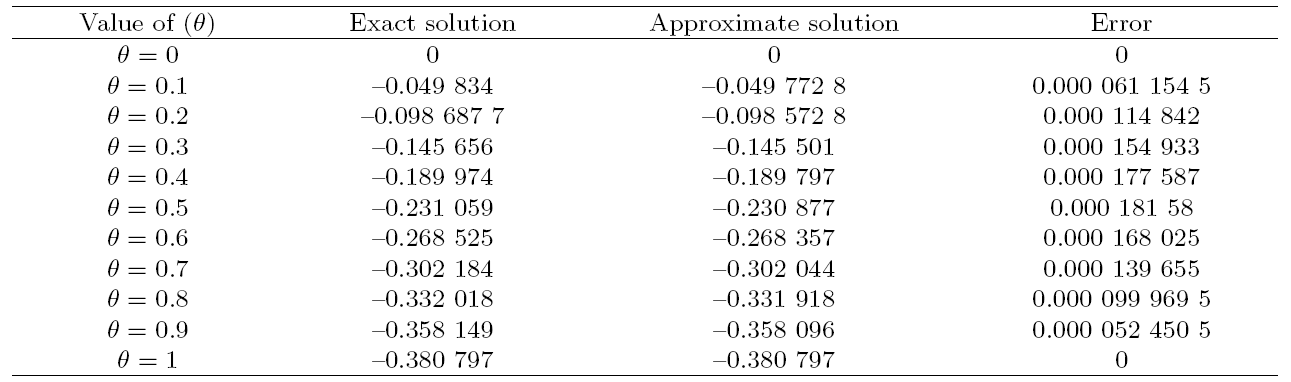
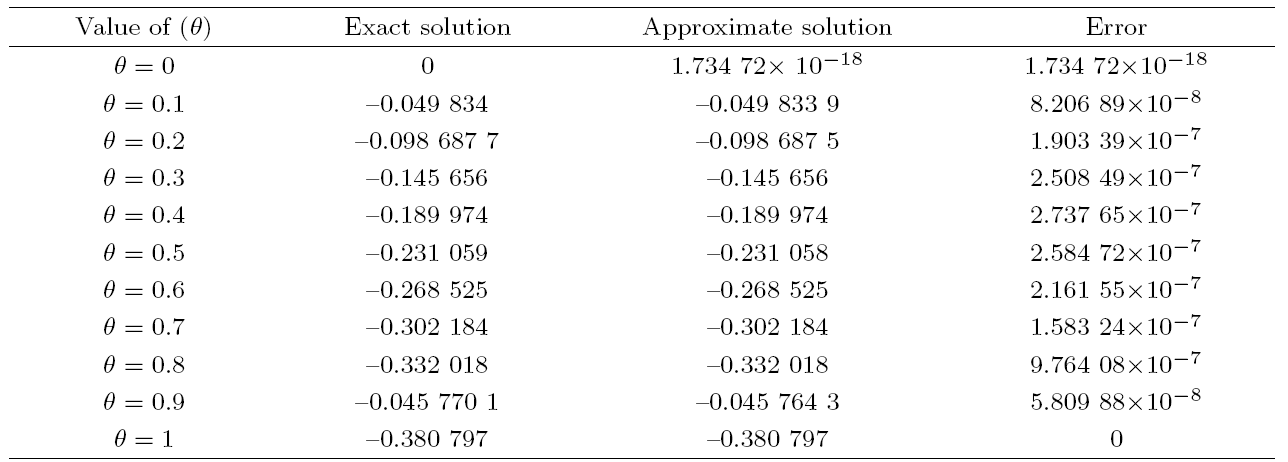
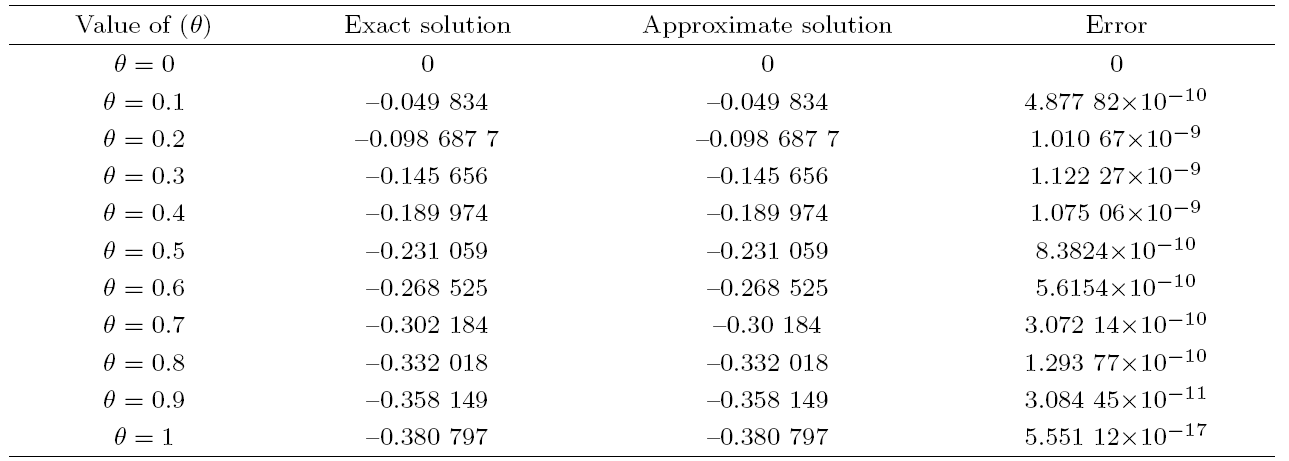
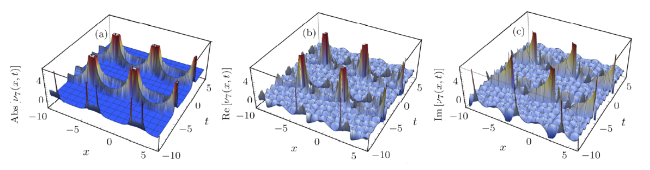
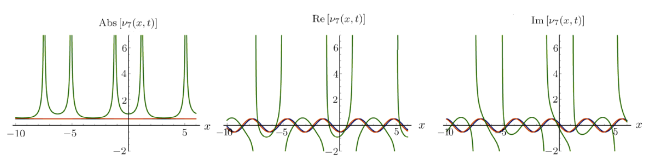
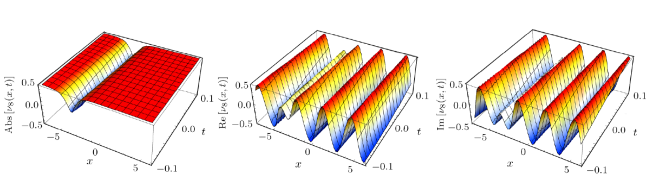
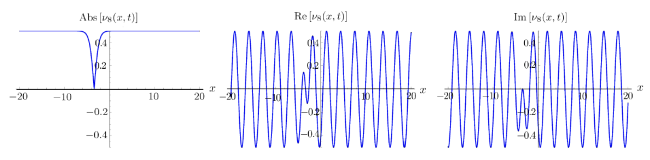
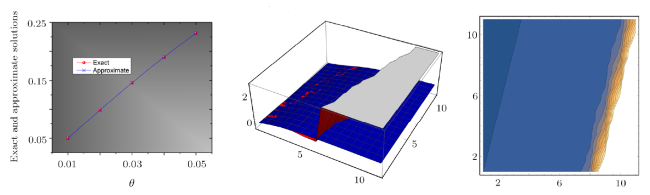
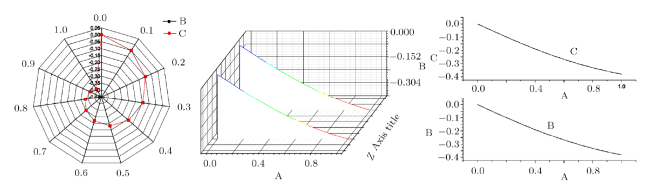
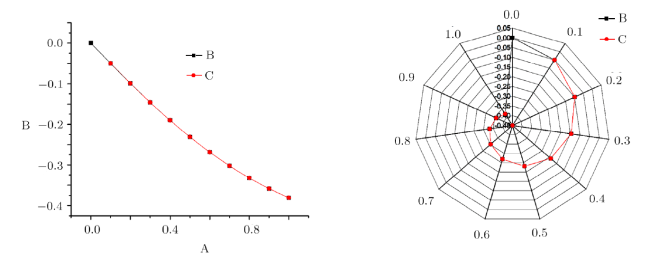
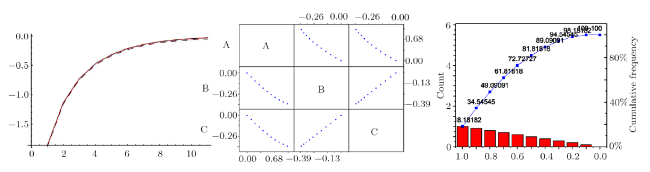
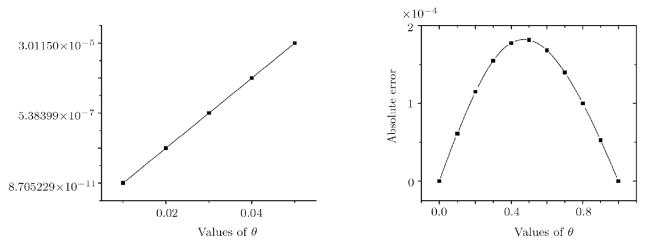
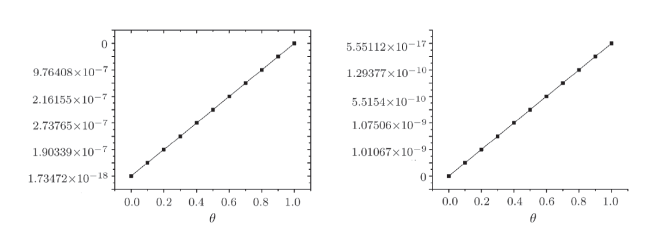
Recently, the nonlinear partial differential equations have been used for modelling many complex natural phenomena such as giant permafrost explosions, desert roses, blood falls, bismuth crystals, synchronized hordes of cicadas, Salar de Uyuni, Pele's hair lava, penitentes, aka fire tornadoes, fire whirls, halos, fire rainbows, volcanic lightning, and so on. Many analytical methods have been derived to study the explicit wave solutions of these complex phenomena that help in testing the accuracy of numerical schemes. It is also considered as a motivation for discovering more accurate numerical schemes that study the approximate solutions of these phenomena. For achieving this goal, the exact analytical wave solutions methods have experienced significant fast growth of development. Many methods have been derived to investigate the analytical and numerical solutions of many phenomena modeling such as modified exp $( -\Phi(\xi)) $ expansion method, generalized auxiliary equation method, $( {G'}/{G}) $-expansion method, Khater method, modified auxiliary equation method (modified Khater method), generalized Kudryashov method, generalized Riccati expansion method, generalized tanh-function method, improved Bernoulli subequation function, improved F-expansion method, sinh-cosh method, and so on.
[1-15]