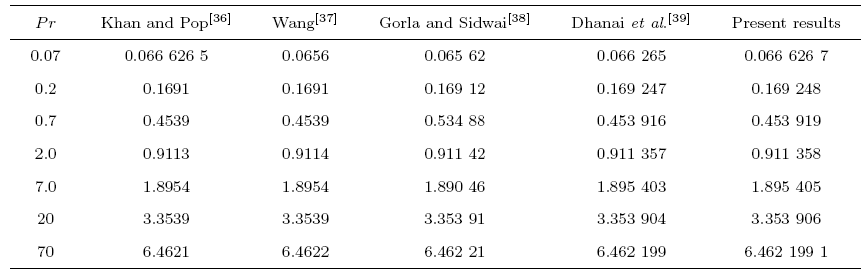
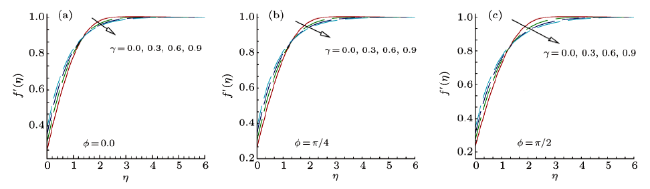
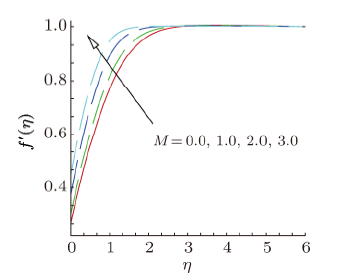
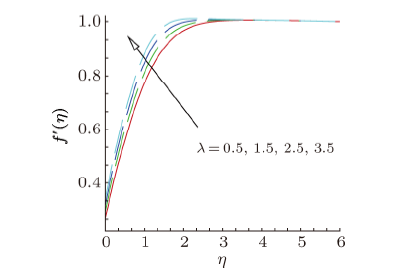
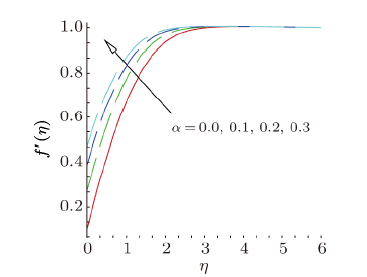
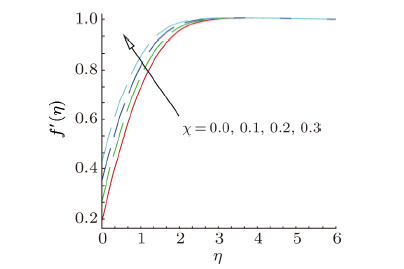
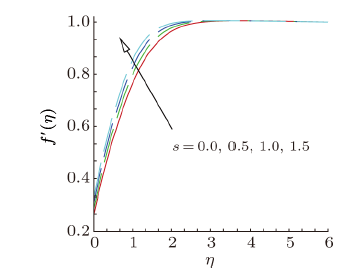
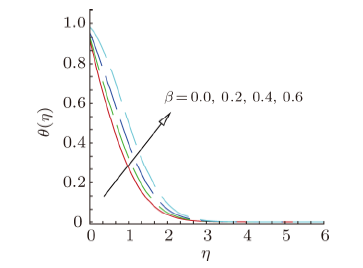
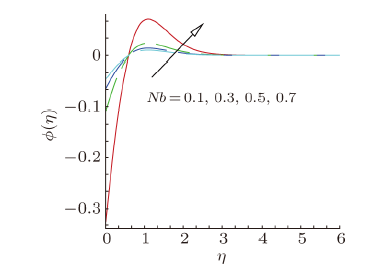
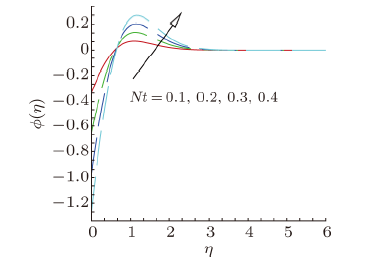
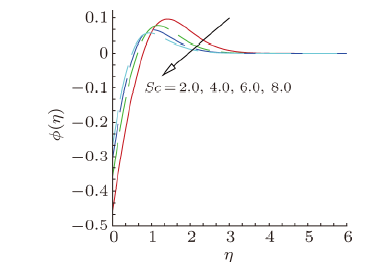
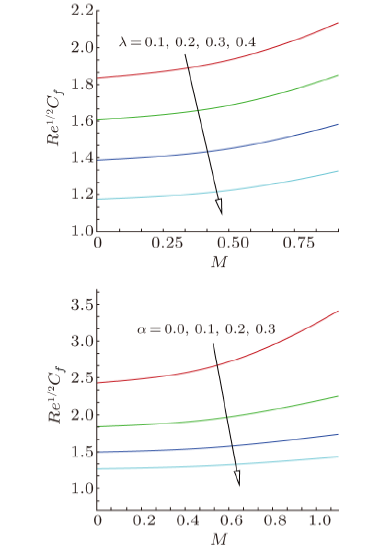
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is the investigation of the intricate collaboration between the magnetic field and electrically conducting fluids. The MHD of boundary-layer flow past a surface which stretches linearly or non-linearly has been broadly inspected as a result of its few modern applications in different mechanical and chemical industries. The combined effects of buoyancy force, Brownian motion, thermophoresis, magnetic field and convective heating on stagnation-point flow and heat transfer due to a nanofluid flow past a stretching or shrinking sheet are investigated by Makinde et al.
[17] Mukhopadhyay and Mandal
[18] discussed the effects of velocity and thermal slip on MHD mixed convection flow past a permeable sheet. They analyzed that increasing suction parameter declines the surface temperature. Fersadou et al.
[19] studied numerically the problem of MHD mixed convection around a porous channel in the presence of nanofluid. They found that heat transfer rate is increased with the higher nanoparticles volume fraction.Hayat et al.
[20] examined the characteristics of MHD mixed convection flow of Ag-water nanofluid past an inclined stretched cylinder in the presence of nonlinear thermal radiation. Later, Waqas et al.
[21] addressed the MHD flow of icropolar fluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet by considering viscous and Joule dissipation effects. Their study reveals that the temperature of the fluid and related boundary layer thickness increases with the enhancement in Prandtl number. In an another paper, Ibrahim et al.
[22] explored the magnetic field and mixed convection effects on Casson nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet. They reported that the local skin friction coefficient decline with Casson parameter. Haq et al.
[23] explored the different aspects of MHD mixed convection flow along a vertical stretching sheet. They illustrated that velocity of the fluid increases with the rising values of power index. Further, Daniel et al.
[24] examined the MHD mixed convection unsteady flow induced due to nanofluid past a permeable stretching surface. Their investigation show that the buoyancy ratio parameter declined the thermal and concentration profiles. Very recently, Sharma et al.
[25] examined the MHD mixed convective low past a vertical stretched surface in the presence of heat generation/absorption effects. Their results indicated that rate of heat transfer increases due to rise in velocity ratio parameter.