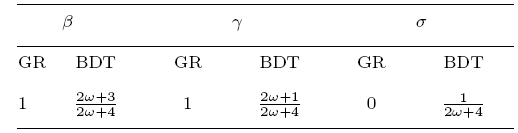
where the metric has signature of ($-+++$), and $m$ denotes the mass of body. The gravitational constant and the light speed in vacuum have been set as $1$. Latin indices $i$ and $j$ run from 1 to 3.$r\equiv |{x}|$ with ${x}\equiv(x^1, x^2, x^3)$ denoting the position vector of the field point $r\!\equiv\! |{x}|$ denotes the distance from the field position ${x}\!\equiv\!(x^1,x^2,x^3)$ to the body located at the coordinate origin. The PPN framework are characterized by the parameters $\alpha$, $\beta$, $\gamma$, $\sigma$, $\epsilon$ and $\varepsilon$.The parameter $\alpha$ is usually absorbed into the definition of the gravitational constant, while we keep it here for the completeness of a general second-order PPN metric, as Ref.
[29] did for the general PPN acceleration. $\beta$, $\gamma$ and $\epsilon$ are the conventional PPN parameters.
[16] The parameter $\varepsilon$ is introduced in Ref.
[27] to include more gravitational theories. The discussions of the physical motivation for this parameter can be found in Refs.
[25, 27] so we do not repeat them here. The parameter $\sigma$ is newly introduced in this work.
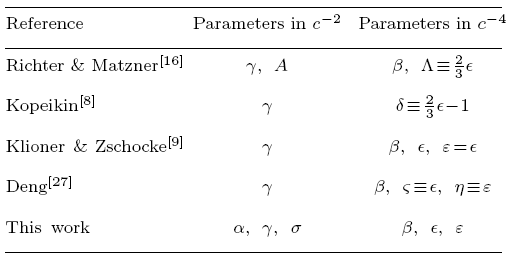
Table 1 lists some representative PPN frameworks of the static spherically-symmetric body's field for light propagation. The relations between the parameters in these references and ours are also shown for readers' convenience.