Consider incident Nd:YAG laser beam with frequency and the spot size as $\omega=1.778\times{}10^{15}$ rad/s and $r_0=80.82 \mu$m to do the numerical analysis. Equations (10), (11), and (12) have been solved to study the effects of exponential density ramp and decentered parameter on self-focusing of the HchG laser beam for mode indices $m$=0, 1, and 2. Presently we have taken the plasmas density ramp as $n(\xi)=n_0\exp(\xi/d)$ having initial electron density as $n_0=0.503\times{}10^{21}{\rm cm}^{-3}, d=0.05$. Here
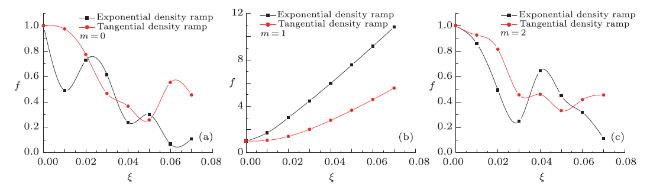
Fig. 1 shows the comparative study of dependence of the beam width parameter ($f$) on normalized distance of propagation ($\xi$) for mode indices $m=0, 1$, and 2 with exponential and tangential plasma density ramps. In
Fig. 1(a), one may notice the effect of exponential density transition in comparison to tangential density ramp on the relativistic self-focusing of the HchG laser beam through magnetoplasma. Similar results with localized upward plasma density transition for the relativistic self-focusing of highly intense laser were shown by Gupta $et al.$
[26] where the stronger self-focusing occurs nearly at $\xi=0.5$. In this manuscript, strong self-focusing of the HchG laser beam occurs at $\xi=0.06$. In the similar way for $m$=1, in
Fig. 1(b), it is noticed that, the beam passing through plasma with exponential as well as tangential density transition gets diffracted. In
Fig. 1(c), strong self-focusing with early effects is noticed for $m=2$. Previously, Kant $et al.$
[27] have observed self-focusing of a laser beam with ponderomotive nonlinearity under plasma density transition and found strong self-focusing nearly at $\xi=0.5$. Here in this work, stronger self-focusing is noticed even at lower values of the normalized distance of propagation.