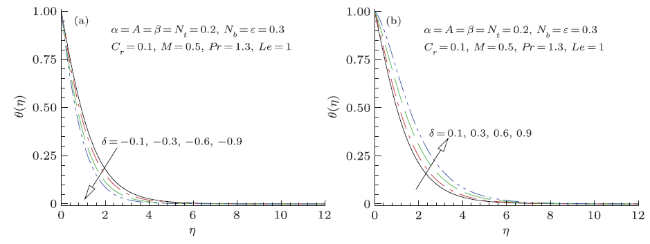
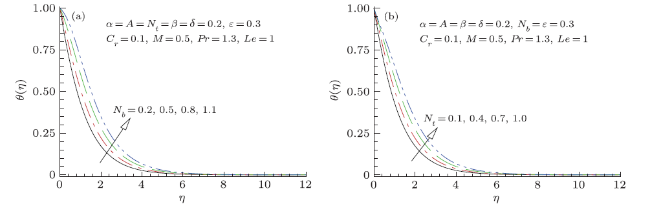
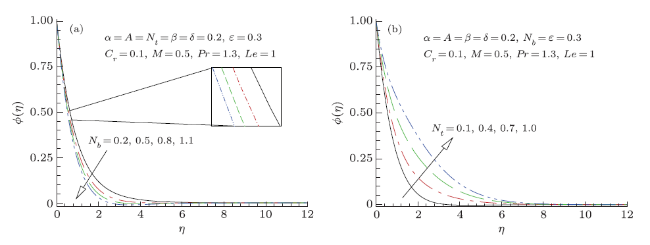
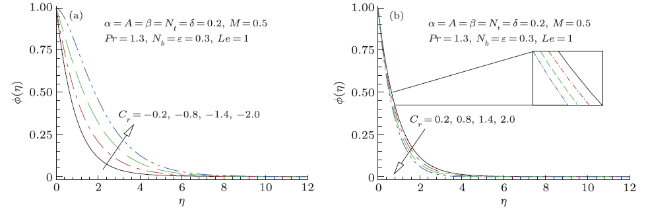
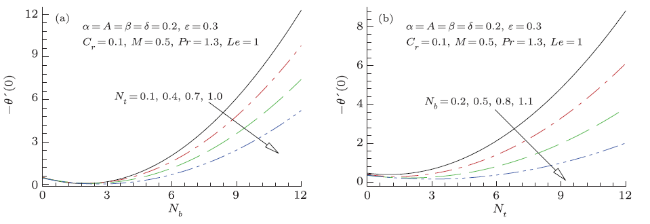
Modern growths in nanotechnology have fetched new discussion of heat transfer liquids acknowledged as nanofluids. Nanofluids are solid-fluid, complex materials prepared of condensed nanoparticles with size (1--100) nm and possess an aptitude of advanced thermal conductivity. These particles, mostly a metal or metal oxide, intensify conduction and convection coefficients, letting for new heat transfer outside the coolant. Owing to their worth in numerous built-up and biomedical applications nanofluids have established thoughtfulness in modern years. Moreover, nanofluids and nanofluids constructed phase conversion materials have been acknowledged as prospective candidate for numerous energy storage and heat transport applications, still they are facing numerous experiments for example pressure drop, stability and extraordinary inflating power. Nano size particle shows a better role in obstructing nanofluid applications; however, the impact of nanoparticles size does not acquire the thoughtfulness as it deserves. The inconsistence and conflict of material provide an impression that the region is not well assumed, thus additional material essential to be prepared. In that instance, overview of nanofluids applications via nanotechnology may be incorporated into each of these technological ranges that are: drag diminutions, nanofluids in boring, magnetic fluids, heating and cooling of constructions, cooling of microchip technology and welding, astral and defense, high-control lasers, warm cylinders and thermal storing. Numerous authors scrutinized critically the applications of nanofluids and acknowledged investigation breakdowns for advance research. Additionally, experiments and forthcoming directions and applications of these liquids with diverse properties have been reviewed and presented in Refs.
[12--20]. In addition, Irfan $et al.$
[21] scrutinized the properties of MHD and heat sink/source in convective flow of Maxwell nanofluid. They inspected that the curvature and Maxwell parameter spectacle conflicting performance on the velocity field while analogous impact on temperature field is being identified. Hayat $et al.$
[22] reported the behavior of thermal radiation and chemical reaction on 3D MHD flow of nanofluid. The non-linear radiative mixed convection flow with deferred nanoparticles in melting surface was studied by Mahantesh $et al.$
[23] Their study indicates that the melting and moving parameters diminish the drag forces or friction. The aspects of activation energy and binary chemical reaction on Williamson nanomaterial was analyzed by Hamid $et al.$
[24] Their upshots specify that the temperature of Williamson fluid intensifies for thermophoresis parameter while the heat transport amount diminishes for reaction parameter.