1. Introduction
2. Basic filter topologies
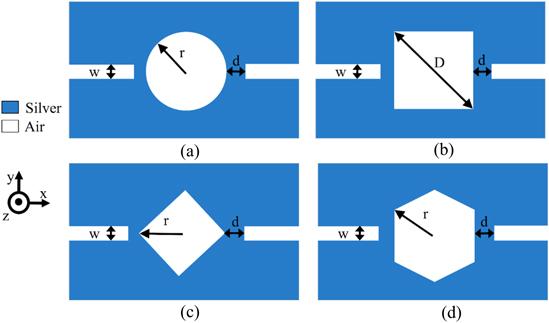
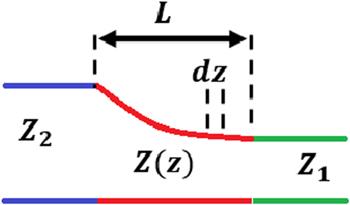
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of plasmonic BPF: (a) with a circular resonator (filter 1), (b) with a square-shaped resonator (filter 2), (c) with a resonator in a form of rhombus (filter 3), (d) with a hexagonal resonator (filter 4). |
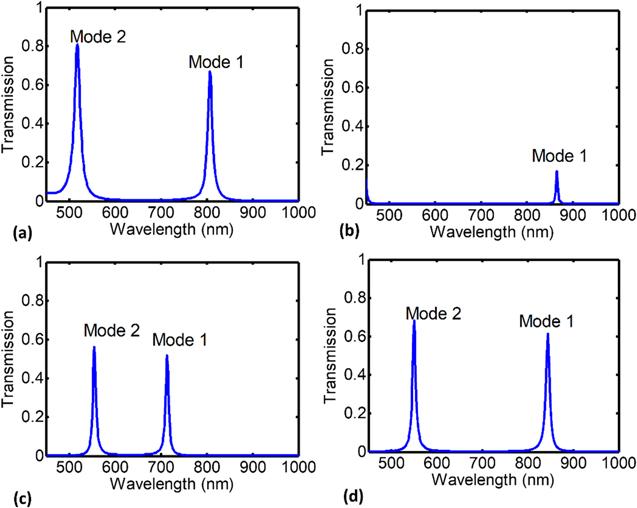
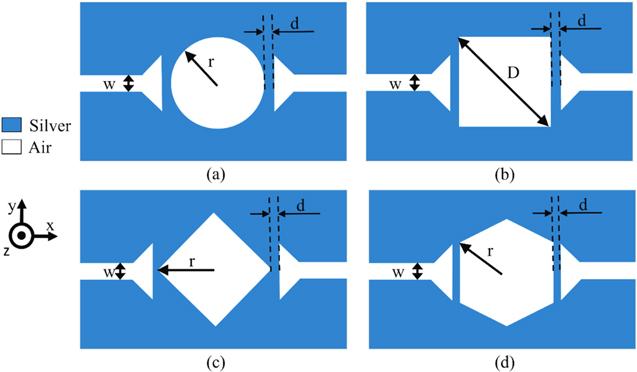
Figure 2. Transmission spectrum of the structures of figure 1 with the primary design which is comprised of two resonance mode using the Drude model: (a) resonator of filter 1 with the radius of r = 200 nm- peak transmission (0.67, 0.81), (b) resonator of filter 2 with the diagonal of D = 510 nm or x-coordinate of vertical edge in 180 nm peak transmission (0.17), (c) resonator of filter 3 with the radius of r = 200 nm- peak (0.52, 0.56), (d) resonator of filter 4 with the radius of r = 230 nm or x-coordinate of vertical edge in 200 nm- peak (0.61, 0.68). |
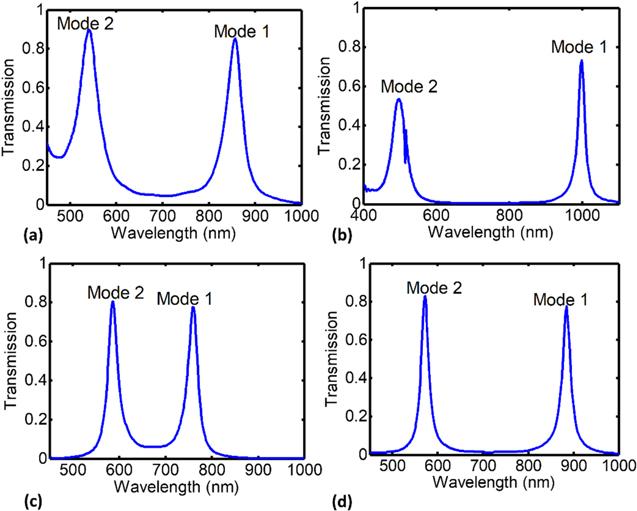
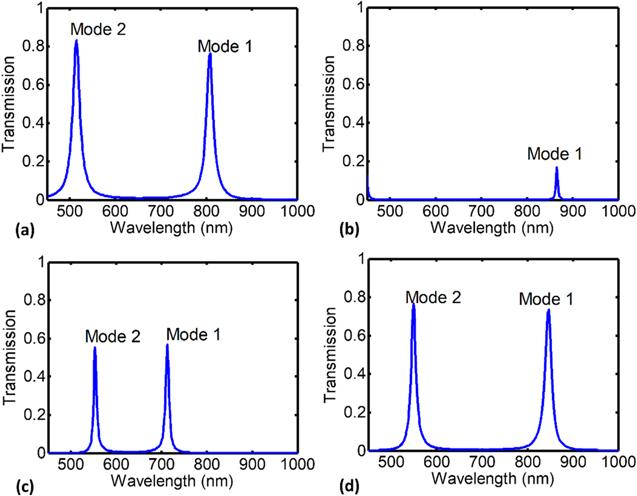
Figure 3. Transmission spectrum of the structures of figure 1 which is comprised of two resonance mode of the maximum possible transmission in the structure in terms of dimension (secondary design): (a) resonator of filter 1 with the radius of r = 210 nm- peak (0.85, 0.897), (b) resonator of filter 2 with the diagonal of D = 594 nm or x-coordinate of vertical edge in 210 nm- peak (0.73, 0.53), (c) resonator of filter 3 with the radius of r = 210 nm- peak (0.78, 0.80), (d) resonator of filter 4 with the radius of r = 240 nm or x-coordinate of vertical edge in 210 nm- peak (0.77, 0.83). |
3. Modeling of the filtering structures
3.1. Drude model
3.2. Drude–Lorentz model
Table 1. Parameters of Drude–Lorentz model for silver. |
| n | ${\omega }_{n}({\rm{THz}})$ | ${\gamma }_{n}({\rm{THz}})$ | ${f}_{n}$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 197.3 | 939.62 | 7.9247 |
| 2 | 1083.5 | 109.29 | 0.5013 |
| 3 | 1979.1 | 15.71 | 0.0133 |
| 4 | 4392.5 | 221.49 | 0.8266 |
| 5 | 9812.1 | 584.91 | 1.1133 |
3.3. Palik model
4. Theoretical investigation
4.1. Main discussion on the theory
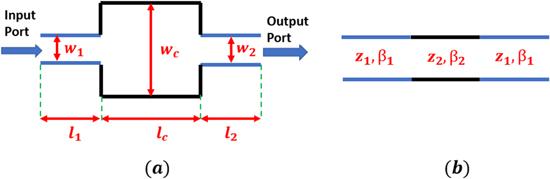
4.2. Theoretical investigation of tapered transmission line (TTL)
Figure 4. (a) Schematic view of MIM junction, (b) equivalent transmission line model. |
Figure 5. Schematic view of equivalent tapered transmission line (TTL). |
5. The proposed structures and their better results
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the proposed filters with triangular-shaped adjunctions in the: (a) first proposed filter with circular resonator (filter 5), (b) second proposed filter with quadratic resonator (filter 6), (c) Third proposed filter with a resonator in a form of rhombus (filter 7), (d) Fourth proposed filter with hexagonal resonator (filter 8). |
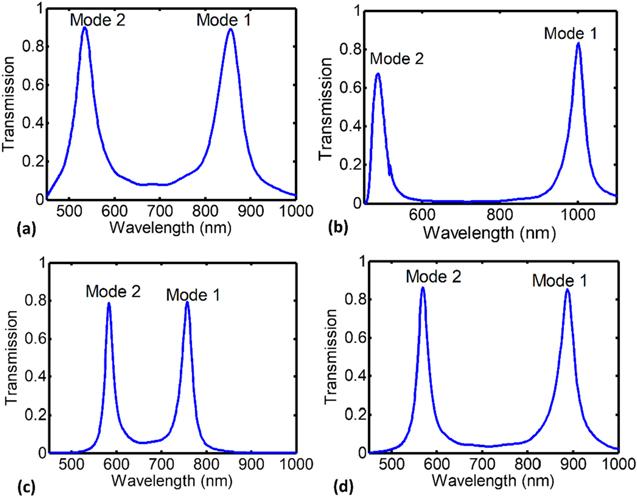
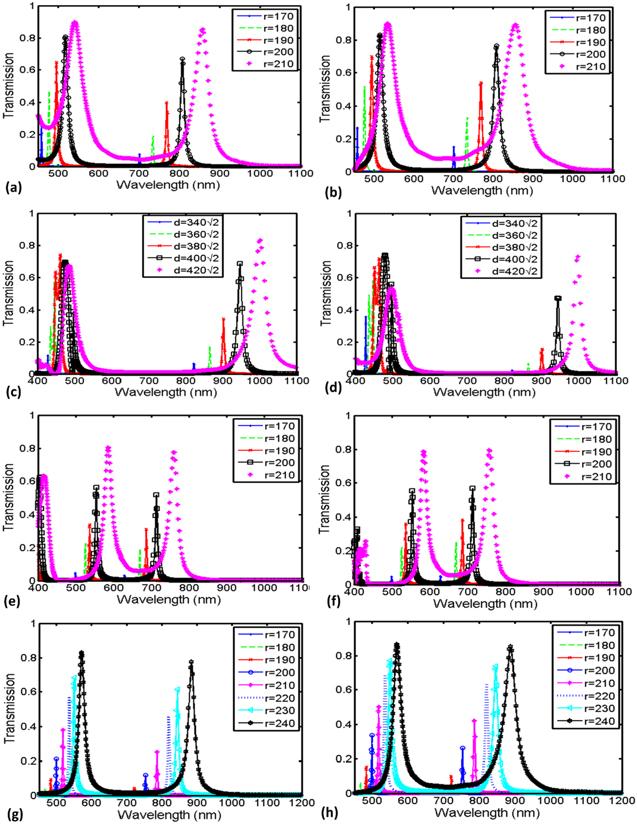
Figure 7. Transmission spectrum of the structures of figure 6 with the primary design of structures mentioned in section |
Figure 8. Transmission spectrum of the structures of figure 6 with the secondary design of structures mentioned in section |
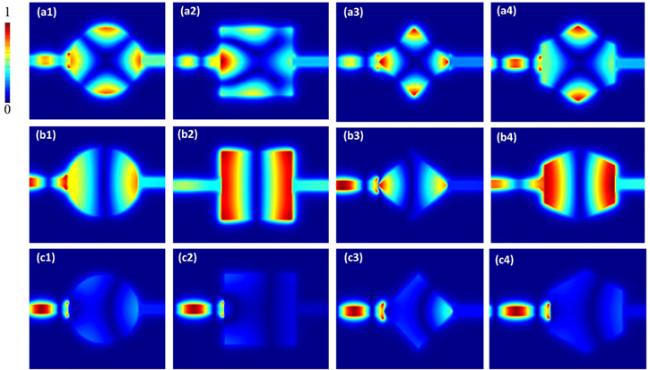
Figure 9. Field distribution of $\left|{{H}}_{{z}}\right|$ for filters with triangular-shaped adjunctions mentioned proposed in figure 6 at the resonance (a), (b) and non-resonance (c) wavelengths of: (1) circular resonator for; (a) λ2 = 515 nm, (b) λ1 = 808 nm, (c) λ = 650 nm. (2) Square-shaped resonator for; (a) λ2 = 482 nm, (b) λ1 = 999 nm, (c) λ = 700 nm. (3) Rhombus-shaped resonator for; (a) λ2 = 582 nm, (b) λ1 = 789 nm, (c) λ = 650 nm. (4) Hexagonal resonator for; (a) λ2 = 568 nm, (b) λ1 = 885 nm, (c) λ = 700 nm. |
6. Parametric study on proposed filters
6.1. Effects of the size of resonators
Figure 10. Comparison of transmission of these four proposed filters with or without triangular-shaped adjunctions by applying different parameters in them with: 1-circular resonator (a) without triangular-shaped adjunctions, (b) with triangular-shaped adjunctions; 2-quadratic resonator (c) without triangular-shaped adjunctions, (d) with triangular-shaped adjunctions; 3-rhombus-shaped resonator (e) without triangular-shaped adjunctions, (f) with triangular-shaped adjunctions; 4-hexagonal resonator (e) without triangular-shaped adjunctions, (f) with triangular-shaped adjunctions. |
6.2. Variation of the size of triangular-shaped adjunctions in waveguides
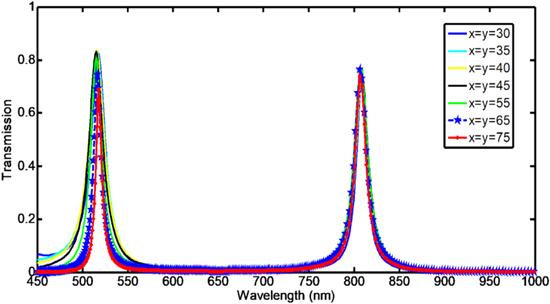
Table 2. Parameters of the first proposed filter with triangular-shaped adjunction. |
| $r({\rm{nm}})$ | $d({\rm{nm}})$ | $w({\rm{nm}})$ | $x({\rm{nm}})$ | $y({\rm{nm}})$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 20 | 50 | 30–75 | 30–75 |
Figure 11. Transmission spectrum for different values of the triangle's edges (‘x' and ‘y'). |
6.3. Fabrication tolerances
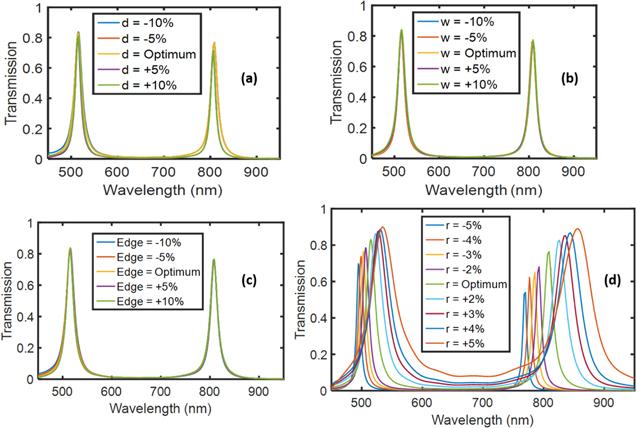
Figure 12. Deviation of different parameters on fabrication tolerances such as; (a) distance (b) width (c) edge (d) radius of the resonator. |
7. Results and comparisons
Table 3. Different parameters of our new designed filters and previous topologies. |
| References | Year | M | $\lambda $(nm) | Maximum transmittance (%) | Q-factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [58] | 2010 | 2 | 520 and 816 | 82.3 and 60 | 32.5 and 54.4 |
| [72] | 2011 | 2 | 655 and 1276 | 34 and 41 | 7.2 and 7.1 |
| [38] | 2011 | 2 | 583.5 and 1145 | 51 and 39 | 11.67 and 14.31 |
| [73] | 2013 | 2 | 829 and 1465 | 52.6 and 29.4 | 23.68 and 41.86 |
| [64] | 2013 | 2 | 517.3 and 803.4 | 74.3 and 45.7 | 64.66 and 114.7 |
| [74] | 2013 | 3 | 595 and 880 and 1550 | 11.85 and 55.45 and 88.66 | 9.15 and 11.89 and 25 |
| [75] | 2014 | 2 | 956 and 1550 | 80.7 and 72.3 | 25.83 and 28.18 |
| [76] | 2014 | 2 | 1110 and 1210 | 64.8 and 70.8 | 11.32 and 14 |
| [77] | 2015 | 1 | 940 | 89.8 | 23.5 |
| [78] | 2016 | 2 | 935 and 1626 | 75.3 and 58 | 21.25 and 35.21 |
| [79] | 2016 | 4 | 449 and 540 and 712 and 114 | 71.6 and 61 and 69 and 41 | 44.9 and 38.5 and 44.5 and 8.1 |
| Filter 1 | 2019 | 2 | 541 and 857 | 85 and 89.7 | 20.4 and 10.4 |
| Filter 2 | 2019 | 1 | 496 and 999 | 73 and 53 | 45.4 and 10.8 |
| Filter 3 | 2019 | 2 | 586 and 759 | 78 and 80 | 29.2 and 23 |
| Filter 4 | 2019 | 2 | 572 and 885 | 77 and 83 | 38.5 and 28.6 |
| Filter 5 | 2019 | 2 | 515 and 808 | 89 and 90 | 13.25 and 12.6 |
| Filter 6 | 2019 | 2 | 482 and 999 | 83 and 67 | 32.2 and 13.4 |
| Filter 7 | 2019 | 2 | 582 and 789 | 79 and 78 | 28.7 and 26.45 |
| Filter 8 | 2019 | 2 | 568 and 885 | 85 and 86 | 22.7 and 20.65 |