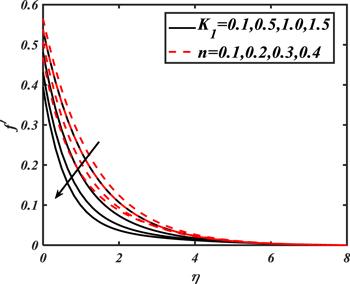
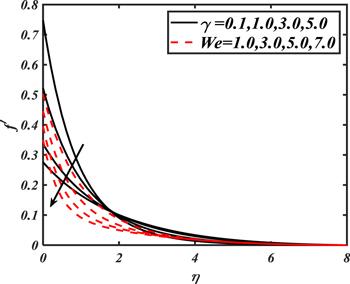
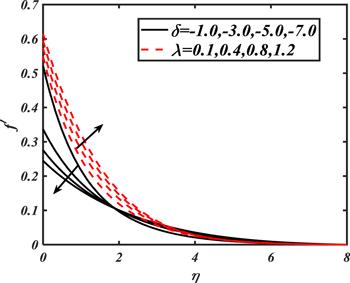
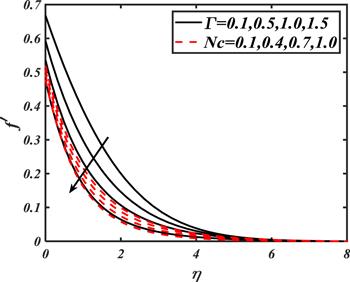
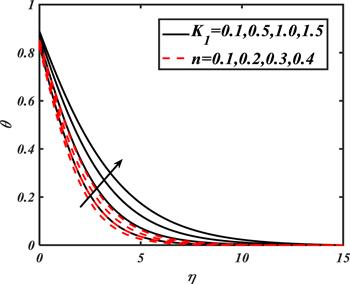
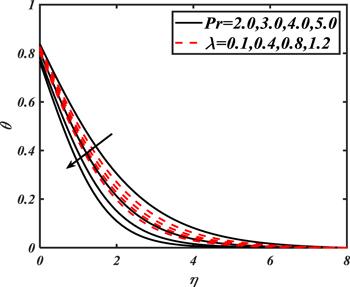
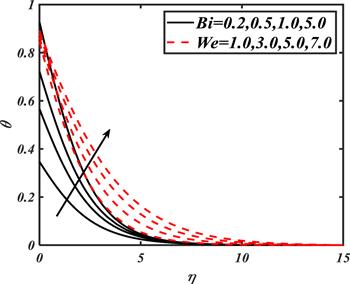
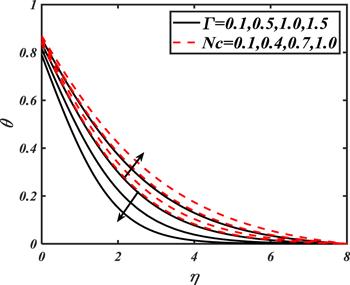
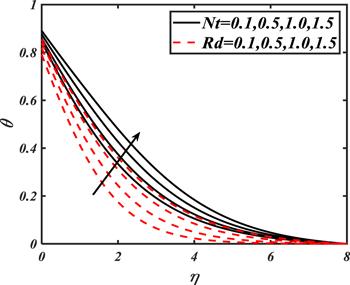
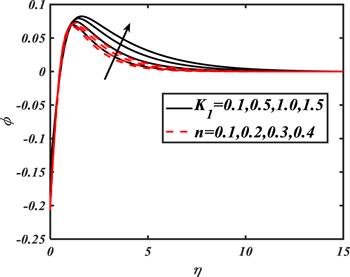
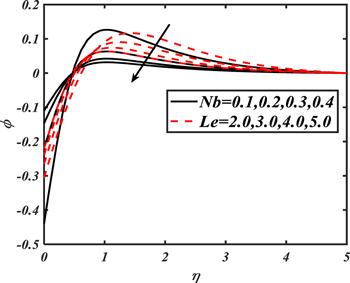
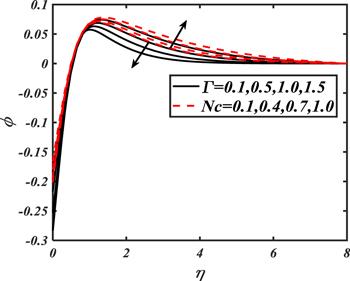
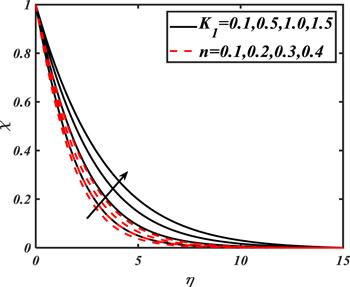
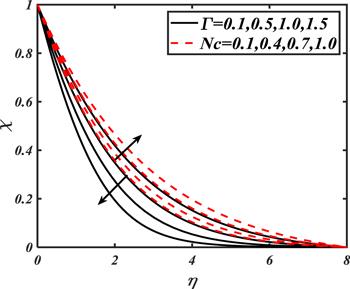
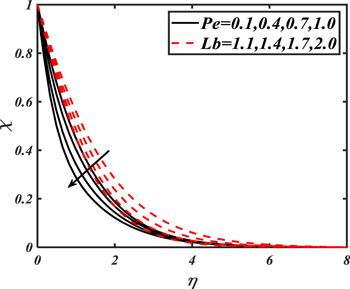
Due to the rapid commercial, engineering and industrial significance of nanofluids, a fundamental interest has been developed by numerous researchers in recent days. The nanoparticles, a complex mixture of nano-sized particles (1-100 nm), attained highly improved thermo-physical features. Due to excellent enhanced resistance and miscellaneous characteristics, nanoparticles are efficiently used in mechanical, industrial, chemical and biological sciences such as cooling of various electronic chips, thermal reactors, chemical processes, fission reactions, sensor technology, catalysis, diagnoses and treatment of cancer tissue, brain tumors, antibacterial applications and many more. The fundamental applications of nanoparticles in thermal extrusion systems also overcome the attention of poor energy reservoirs. From the literature surveyed, it is noted that basic investigation on nanofluids was proposed by Choi [
1]. This involuntary idea insisted scientists perform further interesting contributions in the flow of nanofluids in the presence of some unique flow features. For instance, Sheikholeslami
et al [
2] studied the forced convection flow of nanoparticles subjected to a magnetic field by utilizing the Lattice Boltzmann technique. Khan
et al [
3] analyzed the wedge flow of a Carreau nanofluid with the existence of heat absorption and generation features by employing the shooting technique. The combined heat and mass transportations based on modified Cattaneo-Christov theories in the flow of viscoelastic nanoparticles over a moving geometry was scrutinized by Hayat
et al [
4]. Mahanthesh
et al [
5] analyzed the mixed convective flow over a rotating frame with evaluation of Hall current effects. Siddiqui and Turkyilmazoglu [
6] initiated an interesting contribution based on the flow of ferro-nanoparticles in a cavity. Hsiao [
7] performed a theoretical model based on the flow of micropolar nanoparticles in the presence of viscous dissipation characteristics over a moving surface. The flow of rate type nanoliquid with a heat source and sink features over a rotating disk has been thrashed out numerically by Ahmed
et al [
8]. The study of graphene-water nanoparticles over a stretching/shrinking surface subject to suction and injection characteristics was examined by Aly [
9]. The stability analysis for each critical value was determined and various results have been reported graphically. Rout and Mishra [
10] performed a comparative study regarding magnetized nanoparticles over a moving surface. The interaction of SA-Al
2O
3 and SA-Cu nanoparticles with chemical reaction effects and slip features was reported by Tlili
et al [
11]. Hayat
et al [
12] studied a second grade nanofluid in two parallel disks where magnetic field effects were proposed perpendicularly. Khan and Shehzad [
13] captured the Brownian motion and thermophoresis features in a third grade nanofluid over an accelerated surface. The flow of Maxwell viscoelasticity-based nanoparticles in the presence of slip consequences was specified numerically by Waqas
et al [
14]. Sheikholeslami
et al [
15] investigated the forced convective flow of a nanofluid in a three-dimensional enclosure in the presence of a hot cubic obstacle. Shehzad
et al [
16] explored both the magnetic field and porous medium effects on the flow of a micropolar nanofluid configured by a stretched surface. The study of Cross magneto-nanofluid in stagnation point flow of a contracting and expanding cylinder has been recently presented by Ali
et al [
17]. Li
et al [
18] evaluated the characteristics of nanoparticles in a storage finned in the presence of melting heat transfer.