Nomenclature
| $\left(u,v,w\right)$ | Velocity components in $\left({{\rm{ms}}}^{-1}\right)$ |
| $f^{\prime} (\eta )$ | Radial velocity |
| $f(\eta )$ | Axial velocity |
| $g(\eta )$ | Tangential velocity |
| $k$ | Thermal conductivity $({{\rm{Wm}}}^{-1}{{\rm{K}}}^{-1})$ |
| $Pr$ | Prandtl number |
| $A$ | Stretching parameter |
| ${j}_{{\rm{w}}}$ | Mass flux |
| $(\rho {C}_{{p}})$ | Heat capacitance $({\mathrm{kg}{\rm{m}}}^{-1}{{\rm{s}}}^{-2}{{\rm{K}}}^{-1})$ |
| $T$ | Fluid temperature |
| $K$ | Permeability |
| $C$ | Fluid concentration |
| ${k}_{{\rm{r}}}^{2}$ | Reaction rate $\left({{\rm{s}}}^{-1}\right)$ |
| ${E}_{{\rm{a}}}$ | Activation energy |
| $E$ | Non-dimensional activation energy |
| ${k}^{* }$ | Boltzmann constant $({{\rm{JK}}}^{-1})$ |
| ${a}_{1}$ | Stretching constant |
| $P$ | Pressure |
| ${C}_{{\rm{f}}}$ | Skin friction coefficient |
| ${Re}$ | Reynolds number |
| $Sc$ | Schmidt number |
| $Ec$ | Eckert number |
| $D$ | Mass diffusivity $({{\rm{m}}}^{2}{{\rm{s}}}^{-1})$ |
| $M$ | Magnetic parameter |
| ${\tau }_{{\rm{wt}}}$ | Radial stress |
| ${q}_{{\rm{w}}}$ | Heat flux |
| $Sh$ | Sherwood number, |
| $Nu$ | Nusselt number |
| ${B}_{0}$ | Strength of magnetic field |
| ${\tau }_{{\rm{w}}\phi }$ | Transverse shear stress |
| Greek symbols | |
| $\theta $ | Non-dimensional temperature |
| $\sigma $ | Electrical conductivity $\left({\rm{k}}{{\rm{g}}}^{-1}{{\rm{m}}}^{-3}{{\rm{s}}}^{3}{{\rm{A}}}^{2}\right)$ |
| $\eta $ | Transformed coordinate |
| ${\varnothing }_{1},{\varnothing }_{2}$ | Volume concentration |
| ${\rm{\Omega }}$ | Constant angular velocity $\left({{\rm{s}}}^{-1}\right)$ |
| $\nu $ | Kinematic viscosity $({{\rm{m}}}^{2}{{\rm{s}}}^{-1})$ |
| $\varepsilon $ | Pressure parameter |
| $\delta $ | Temperature difference |
| $\mu $ | Dynamic viscosity $({\rm{kg}}\,{{\rm{s}}}^{-1}{{\rm{m}}}^{-1})$ |
| $\rho $ | Density $({{\rm{kgm}}}^{-3})$ |
| Subscript | |
| ${\rm{f}}$ | Fluid |
| ${\rm{bf}}$ | Base fluid |
| ${\rm{hnf}}$ | Hybrid nanofluid |
| ${{\rm{s}}}_{1},{{\rm{s}}}_{2}$ | Solid particle |
| $\infty $ | Ambient |
| ${\rm{w}}$ | Surface |
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical formulation
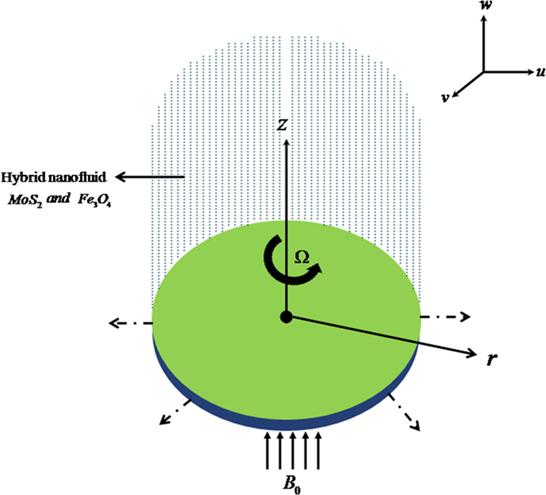
Figure 1. Flow configuration. |

3. Result and discussion
Table 1. Thermo-physical properties of nanoparticles. |
| Physical properties | Base fluid ${{\rm{H}}}_{2}{\rm{O}}$ | Nanoparticles ${{\rm{MoS}}}_{2}$ | Nanoparticles ${{\rm{Fe}}}_{3}{{\rm{O}}}_{4}$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density $\rho ({\rm{kg}}\,{{\rm{m}}}^{-3})$ | 997.1 | 5060 | 5180 |
| Specific heat ${c}_{{p}}({\rm{J}}/{\rm{kgK}})$ | 4179 | 397 | 670 |
| Thermal conductivity $k({\rm{W}}\,{{\rm{mK}}}^{-1})$ | 0.613 | 904.4 | 9.7 |
| Electrical conductivity $\sigma {\left({\rm{\Omega }}{\rm{m}}\right)}^{-1}$ | $5.5\times {10}^{-6}$ | 2090 | 25 000 |
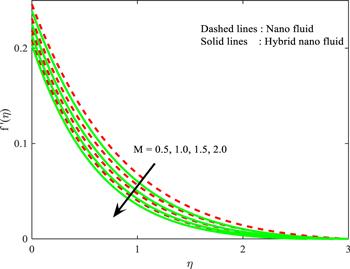
Figure 2. Influence of $M$ on $f^{\prime} \left(\eta \right).$ |
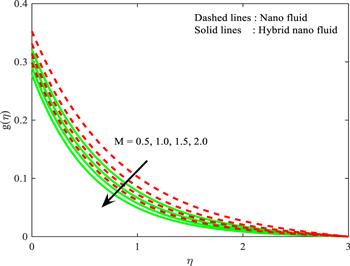
Figure 3. Influence of $M$ on $g\left(\eta \right).$ |
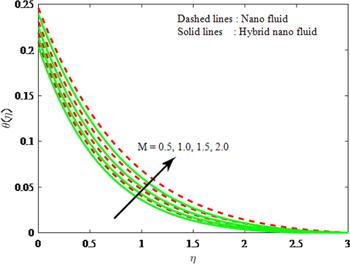
Figure 4. Influence of $M$ on $\theta \left(\eta \right).$ |
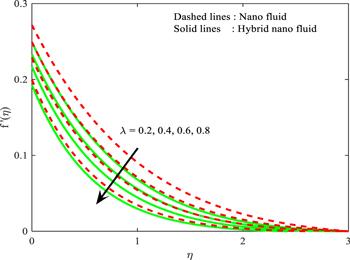
Figure 5. Influence of $\lambda $ on $f^{\prime} \left(\eta \right).$ |
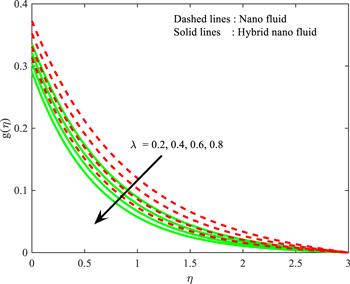
Figure 6. Influence of $\lambda $ on $g\left(\eta \right).$ |
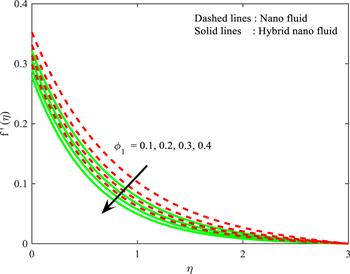
Figure 7. Influence of ${\varnothing }_{1}$ on $f^{\prime} \left(\eta \right).$ |
Figure 8. Influence of ${\varnothing }_{1}\,$on $\theta \left(\eta \right).$ |
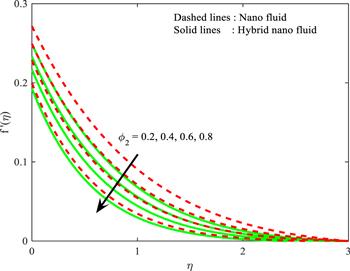
Figure 9. Influence of ${\varnothing }_{2}$ on $f^{\prime} \left(\eta \right).$ |
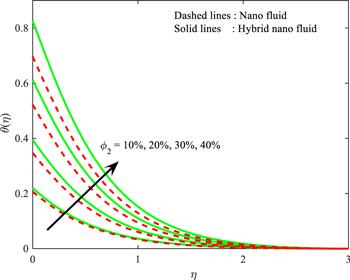
Figure 10. Influence of ${\varnothing }_{2}$ on $\theta \left(\eta \right).$ |
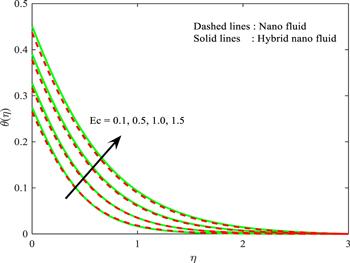
Figure 11. Influence of $Ec$ on $\theta \left(\eta \right).$ |
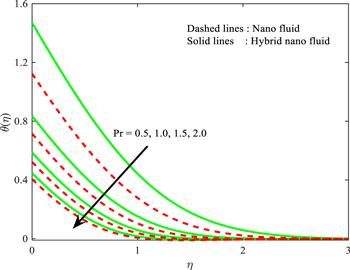
Figure 12. Influence of ${\Pr }$ on $\theta \left(\eta \right).$ |
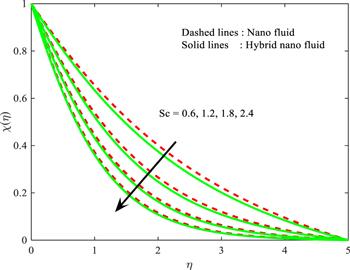
Figure 13. Influence of $Sc$ on $\chi \left(\eta \right).$ |
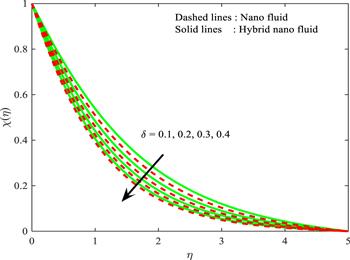
Figure 14. Influence of $\delta $ on $\chi \left(\eta \right).$ |
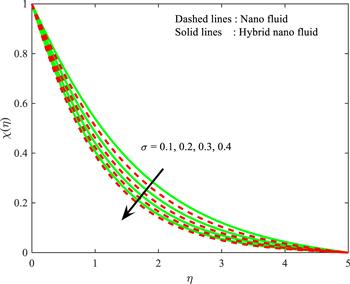
Figure 15. Influence of $\sigma $ on $\chi \left(\eta \right).$ |
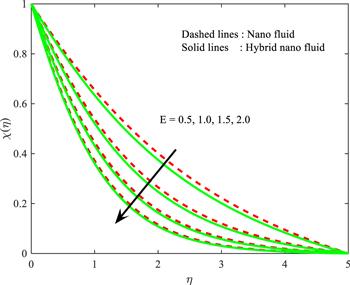
Figure 16. Influence of $E$ on $\chi \left(\eta \right).$ |
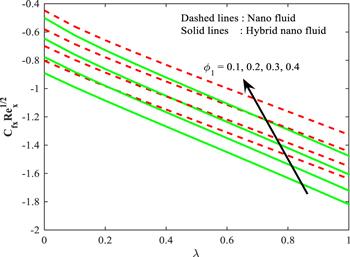
Figure 17. Influence of $\lambda $ versus ${\varnothing }_{1}$ on ${{Re}}^{\tfrac{1}{2}}{C}_{{\rm{fx}}}.$ |
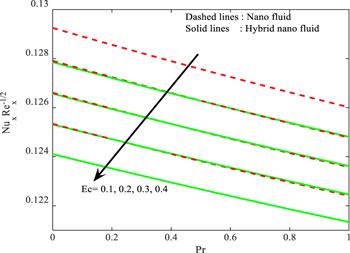
Figure 18. Influence of $Ec$ and ${\Pr }$ on ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Nu.$ |
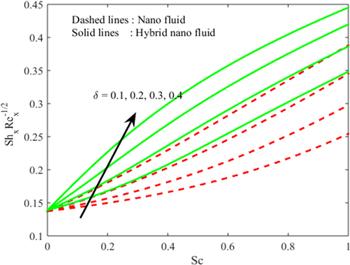
Figure 19. Influence of $\delta $ and $Sc$ on ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Sh.$ |
Table 2. Numerical values of ${{Re}}^{\tfrac{1}{2}}{C}_{{\rm{fx}}}$ for different physical parameter values. |
| ${{Re}}^{\tfrac{1}{2}}{C}_{{\rm{fx}}}$ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $M$ | $\lambda $ | ${\varnothing }_{1}$ | ${\varnothing }_{2}$ | Nanofluid | Hybrid nanofluid |
| 0.5 | −1.127 498 | −1.106 825 | |||
| 1.0 | −1.177 467 | −1.153 211 | |||
| 1.5 | −1.192 089 | −1.192 160 | |||
| 0.1 | 0.977 902 | −1.094 206 | |||
| 0.2 | −−1.084 503 | −1.145 167 | |||
| 0.3 | −1.144 617 | −1.199 912 | |||
| 0.1 | −0.137 800 | −0.184 883 | |||
| 0.2 | −0.122 279 | −0.164 147 | |||
| 0.3 | −0.106 240 | −0.142 617 | |||
| 0.1 | −0.144 872 | −0.157 821 | |||
| 0.2 | −0.125 478 | −0.148 756 | |||
| 0.3 | −0.104 887 | −0.954 71 | |||
Table 3. Numerical values of ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Nu$ for different physical parameter values for both the hybrid and nanofluid case. |
| ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Nu$ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ${\Pr }$ | $Ec$ | $M$ | ${\varnothing }_{1}$ | ${\varnothing }_{2}$ | Nanofluid | Hybrid nanofluid |
| 0.1 | 0.147 526 | 0.166 076 | ||||
| 0.3 | 0.171 266 | 0.166 270 | ||||
| 0.5 | 0.201 602 | 0.201 61 | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.262 315 | 0.171 266 | ||||
| 0.3 | 0.238 968 | 0.166 031 | ||||
| 0.5 | 0.218 061 | 0.161 655 | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.184 255 | 0.179 411 | ||||
| 0.2 | 0.187 977 | 0.180 097 | ||||
| 0.3 | 0.192 973 | 0.183 820 | ||||
| 0.1 | 2.452 295 | 2.457 524 | ||||
| 0.2 | 2.349 007 | 2.359 885 | ||||
| 0.3 | 2.241 073 | 2.258 100 | ||||
| 0.1 | 2.632 48 | 2.527 524 | ||||
| 0.2 | 2.415 200 | 2.429 885 | ||||
| 0.3 | 2.351 073 | 2.338 100 | ||||
Table 4. Numerical values of ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Sh$ for different physical parameter values for both the hybrid and nanofluid case. |
| ${{Re}}^{-1/2}Sh$ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $Sc$ | $\sigma $ | $\delta $ | $E$ | Nano fluid | Hybrid nanofluid |
| 0.1 | 0.594 632 | 0.682 126 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.622 126 | 0.757 120 | |||
| 0.3 | 0.737 120 | 0.833 300 | |||
| 0.1 | 0.228 075 | 0.239 495 | |||
| 0.15 | 0.259 495 | 0.300 374 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.278 075 | 0.319 495 | |||
| 0.1 | 0.378 485 | 0.390 374 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.350 374 | 0.360 687 | |||
| 0.3 | 0.378 485 | 0.390 374 | |||
| 0.01 | 0.250 454 | 0.270 687 | |||
| 0.1 | 0.287 421 | 0.288 215 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.304 821 | 0.314 562 | |||
Table 5. Comparison of of statistical values with Miklavcic and Wang [36] in the absence of $M,$ $\varepsilon ,$ $\lambda $ Pressure gradient, nanoparticles, energy and mass effects. |
| Miklavcic and Wang [36] | Present results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | $\eta $ | $f^{\prime\prime} (0)$ | $g^{\prime} (0)$ | $f^{\prime\prime} (0)$ | $g^{\prime} (0)$ |
| 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.510 232 | −0.615 922 | 0.509 680 | −0.605 830 |
4. Conclusion
| • | enhanced values of $\lambda $ decrease the velocity profile for both cases |
| • | enhancement of heat transfer is greater in hybrid nanoparticles when compared to nanoparticles for different values of $M$ |
| • | $f^{\prime} (\eta )$ and $g(\eta )$ is decreased for enhancing values of both ${\varnothing }_{1}\,\,$and ${\varnothing }_{2}$ |
| • | larger $\sigma $ and $Sc$ reduces the solutal boundary layer |
| • | larger-scale $M$ and $\lambda $ slows down the fluid velocity of both nanoparticle cases |
| • | thermal field enhances for increasing values of both ${\varnothing }_{1}\,\,$and ${\varnothing }_{2}.$ |