1. Introduction
2. The first entanglement witness
For any four-qubit quantum state ρ, a necessary criterion of tripartite separability is $\mathrm{Tr}\left[\rho {\hat{W}}_{1}\right]\geqslant 0$.
Under the partition $| 1| 2| 34| $, the pure state is shown in equation (
$B=-({\xi }_{1}+{\xi }_{2})+\tfrac{d}{3}{\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}({\xi }_{1}^{* }+{\xi }_{2}^{* })$,
$C=1+\tfrac{4d}{3}(| {\xi }_{1}{| }^{2}+| {\xi }_{2}{| }^{2})+\tfrac{d}{3}({\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}^{* }+{\xi }_{1}^{* }{\xi }_{2})$,
$D=-1\,+\tfrac{d}{3}(| {\xi }_{1}{| }^{2}+| {\xi }_{2}{| }^{2})+\tfrac{4d}{3}({\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}^{* }+{\xi }_{1}^{* }{\xi }_{2})$,
$E=\tfrac{4d}{3}{\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}$, $F=\tfrac{4d}{3}$, $H=\tfrac{d}{3}({\xi }_{1}+{\xi }_{2})$. If the following matrix is positive semi-definite:
A necessary condition of tripartite separability for a noisy GHZ-W state is
According to Theorem
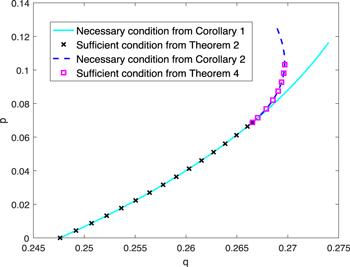
Figure 1. Necessary and/or sufficient criteria for the triseparability of state $\rho =p| \mathrm{GHZ}\rangle \langle \mathrm{GHZ}| +q| {\rm{W}}\rangle \langle {\rm{W}}| +\tfrac{1-p-q}{16}{I}_{16}$. |
For a noisy GHZ-W state, the necessary criterion of tripartite separability in corollary 1 is also sufficient in the parameter interval of ${\rm{\Theta }}\in [0,0.080401\pi ]$.
We try to construct a quantum state ${\rho }_{s}=| {{\rm{\Psi }}}_{s}\rangle \langle {{\rm{\Psi }}}_{s}| $ which meets $\mathrm{Tr}[\hat{W}{\rho }_{s}]=0$ if we obtain an entanglement witness $\hat{W}$, hence we can get the boundary hypersurface distinguishing entangled states from separable states. We then construct a triseparable state using the eigenvectors corresponding to zero eigenvalues of some matrix derived from entanglement witness. In other words, the state which we used to construct the tripartite separable states in the boundary of tripartite separable state set should satisfy $\langle {{\rm{\Psi }}}_{s}| \hat{W}| {{\rm{\Psi }}}_{s}\rangle =0$. At $| {\rm{W}}\rangle $ states side of a noisy GHZ-W state, we construct triseparable states with type ${\rm{I}}:{\xi }_{1}={\xi }_{2}$ and type $\mathrm{II}:{\xi }_{1}=-{\xi }_{2}$, then mix the constructed states in order to offset the off diagonal elements except $| {\rm{W}}\rangle $ state and $| \mathrm{GHZ}\rangle $ state. The process is mainly divided into the following three steps:
3. The second entanglement witness
For any four-qubit quantum state ρ, another necessary criterion of tripartite separability is $\mathrm{Tr}\left[\rho {\hat{W}}_{2}\right]\geqslant 0$.
Under the partition $| 1| 2| 34| $ (see (
Another necessary condition of tripartite separability for a noisy GHZ-W state is
Apply theorem
For a noisy GHZ-W state, the necessary condition of tripartite separability in corollary 2 is also sufficient in the parameter interval of ${\rm{\Theta }}\in [0.080401\pi ,0.11628\pi ]$.
We will construct new states ${\rho }_{{\rm{I}}}$, ${\rho }_{\mathrm{II}}$ and ${\rho }_{\mathrm{III}}$ by using the witness ${\hat{W}}_{2}$. There will be some differences in the treatments of diagonal elements of the states between witnesses ${\hat{W}}_{1}$ case and ${\hat{W}}_{2}$ case. Taking the state ρ in equation (