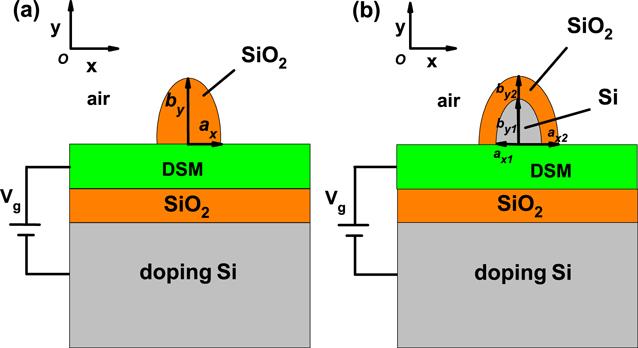
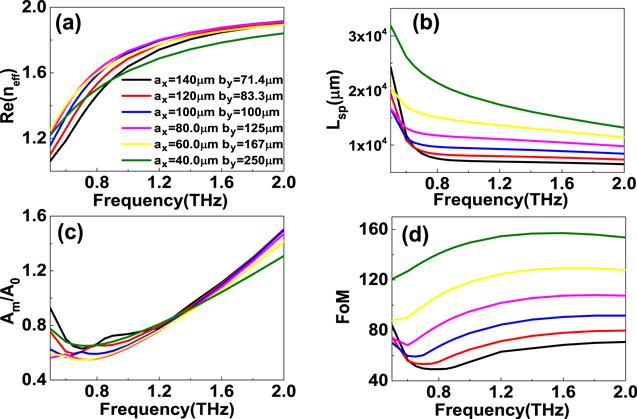
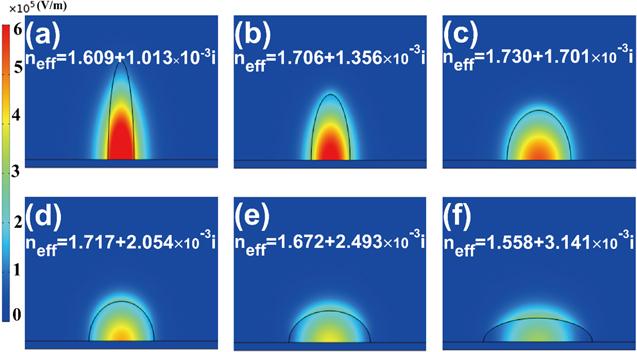
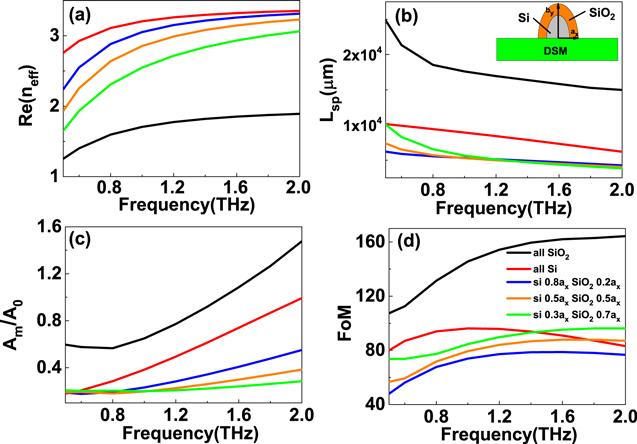
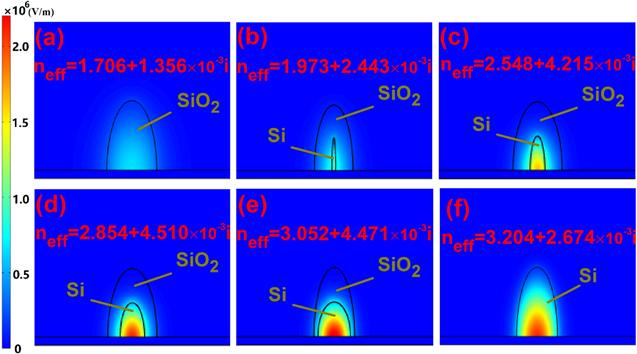
The numerical results have been obtained using the finite element method (FEM) software package-COMSOL MULTIPHYSICS 4.2. The propagation properties of the suggested 3D DSM DLSPs waveguides are shown in figure
2. To have a fair comparison, the cross-sectional areas of semielliptical dielectric fibers are taken as 1 × 10
4 μm
2. The influences of a
x on the Re(
neff) and propagation lengths of hybrid modes can be found in figures
2(a) and (b), respectively. As the frequency increases, the 3D DSM permittivity decreases, and the contribution of plasmonic mode decreases, resulting in the value of the Re(
neff) increasing, and the propagation length decreasing. For example, at the frequencies of 0.5 THz, 1.0 THz, and 2.0 THz, the 3D DSM permittivity are −1.850 × 10
4 + 1.310 × 10
4i, −6.162 × 10
3 + 2.186 × 10
3i and −1.672 × 10
3 + 299.5i, respectively. Correspondingly, the values of Re(
neff) of hybrid modes are 1.157, 1.720 and 1.914, and the propagation lengths are 1.665 × 10
4 μm, 9.443 × 10
3 μm, and 8.417 × 10
3 μm, respectively. In addition, the semielliptical fiber shape also affects the propagation property significantly. It can be found in figure
2(a), that if the value of the semi-minor axis of dielectric semielliptical fiber is small,
i.e. ax < 80
μm, the length of semielliptical fiber along the
y direction,
by, is large, the mode can be better confined. As the value of
ax (
by) increases (decreases), some modes leak into the surrounding air, and the real part of the effective index decreases. For example, at the frequency of 1.0 THz, if the value of a
x is 60, 100 and 120
μm, the values of the Re(
neff) are 1.708, 1.720 and 1.686, and the propagation lengths are 1.423 × 10
4 μm, 9.443 × 10
3 μm, and 8.070 × 10
3 μm, respectively. The mode confinement can be well measured by the normalized effective mode area
Am/
A0, in which
A0 is the diffraction-limited area, and the value is
λ2/4. As the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases, and the contribution of fiber mode increases, thus the 3D DSM-supported DLSPs show weak mode confinement at a large frequency, as given in figure
2(c). As the frequency increases, the permittivity of the 3D DSM layer decreases, the influence of the plasmonic mode reduces, and the contribution of dielectric fiber mode increases, resulting in the mode area increasing. To judge the comprehensive performance of mode confinement and dissipation of the hybrid modes, the definition of FoM is given by equation (
9). As the frequency increases, the contribution of the low lossy fiber mode increases, while the effects of high dissipation plasmonic mode decrease, resulting in the value of FoM increasing. It is clear that the FoM is also closely associated with the fiber shape. As shown in figure
2(d), as the value of
ax decreases, the semielliptical fiber becomes sharper, and the interaction area of fiber with the 3D DSM layer reduces, thus the 3D DSM structure manifests better mode confinement and a larger value of FoM.