1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. DNA hairpin structure design
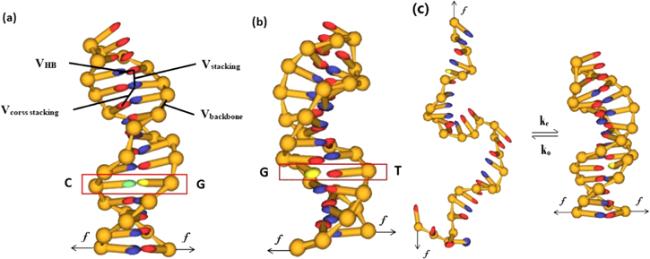
Figure 1. Illustration of the hairpin structure in the ox-DNA model and dynamic transition of the DNA hairpin structure under a stretching force. (a) DNA hairpin with 11 AT base pairs and one GC base pair in the stem and 4T bases in the loop. (b) The GC base pair in the stem of the DNA hairpin is replaced by a G:T mismatch. (c) The folded/unfolded transition of the DNA hairpin structure with a G:T mismatch in its stem under a stretching force. |
Table 1. Different sequences of DNA hairpin with 15 base pairs in the stem. Sequence indexed by (0) represents the DNA hairpin without a DNA mismatch in the stem, as a comparison, the sequence indexed by (n) indicates that the original GC base pair at position n from the hairpin loop is replaced by DNA mismatch G:T. |
| Index | Sequence |
|---|---|
| (0) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAA G TATAA T4 TTATA C TTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (1) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAATTATA G T4 T TATAATTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (2) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAATTAT G A T4 T T ATAATTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (3) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAATTA G AA T4 TT T TAATTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (4) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAATT G TAA T4 TTA T AATTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (5) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAAT G ATAA T4 TTAT T ATTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (6) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAAA G TATAA T4 TTATA T TTTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (7) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTAA G TTATAA T4 TTATAA T TTAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (8) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATTA G ATTATAA T4 TTATAAT T TAATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (9) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATATT G AATTATAA T4 TTATAATT T AATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (10) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AATAT G AAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTT T ATATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (11) | $5^{\prime} $-T4AATA G TAAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTTA T TATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (12) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AAT G TTAAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTTAA T ATT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (13) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 AA G ATTAAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTTAAT T TT T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (14) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 A G TATTAAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTTAATA T T T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
| (15) | $5^{\prime} $-T4 G ATATTAAATTATAA T4 TTATAATTTAATAT T T4-$3^{\prime} $ |
3. Results
3.1. Effects of single base-pair mismatch on DNA hairpin stability
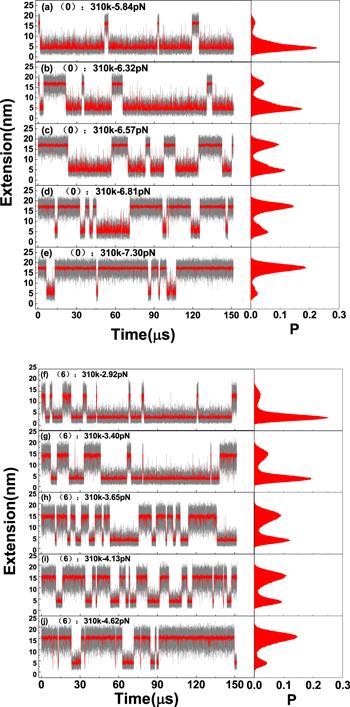
Figure 2. Dynamics of a DNA hairpin with 15 base pairs in the stem at a constant temperature of 310 K and their extension probability distributions in the right panel. (a)–(e), dynamics of a DNA hairpin with sequence (0) under stretching forces from 5.84 to 7.30 pN; (f)–(j), dynamics of a DNA hairpin with sequence (6) under stretching forces from 2.92 to 4.62 pN. |
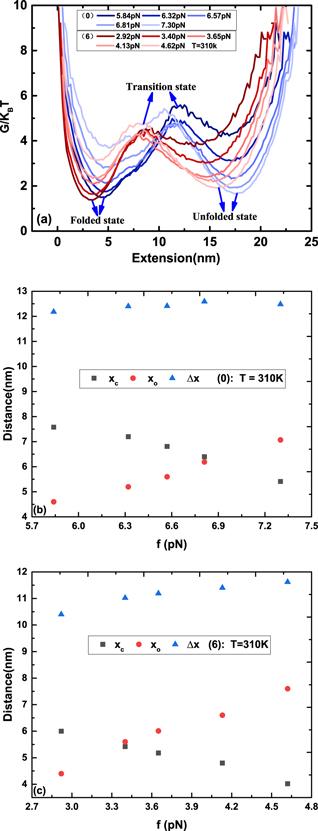
Figure 3. (a) The free energy landscape of DNA hairpins with sequences (0) and (6) under different stretching forces. (b)–(c) The distance to the transition state from the folded state (xc) and the unfolded state (xo) and the distance between folded and unfolded states (ΔX) as a function of stretching force f. (b) and (c) correspond to the sequences (0) and (6), respectively. |
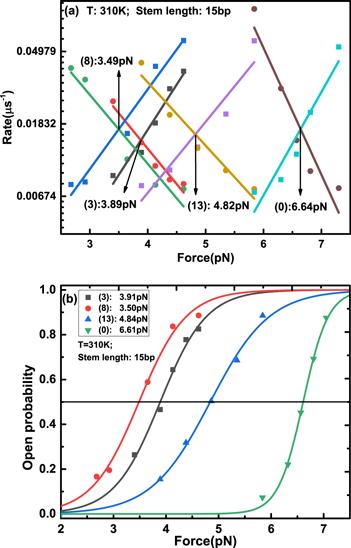
Figure 4. (a) Force-dependent folded rate and unfolded rate of DNA hairpins with different sequences. Their cross points give the critical forces. (b) Force-dependent open probability of DNA hairpins with different sequences. Fitting with the Boltzmann relationship gives the critical forces corresponding to the open probability of 50%, which are consistent with the analysis of the force-dependent folded and unfolded rates of the DNA hairpin in figure 4(a). |
3.2. Identification of the intermediate state caused by DNA mismatch
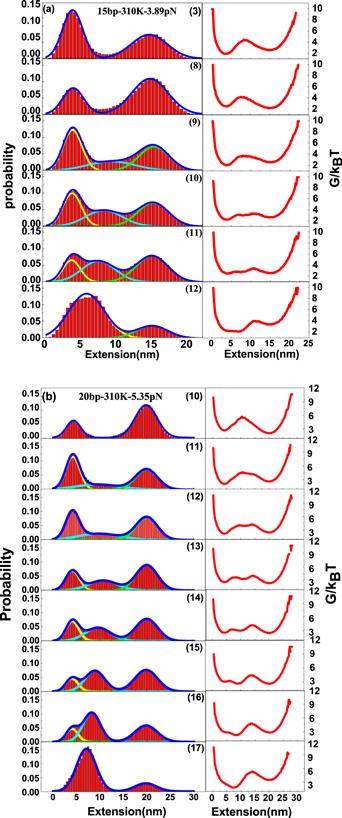
Figure 5. Fitting extension probability distribution of the DNA hairpin with DNA mismatch in the stem and their corresponding free energy landscapes in the right panel. (a) Fitting extension probability distribution of the DNA hairpin with 15 base pairs in the stem. The position of DNA mismatch in the stem ranges from position (3) to (12). (b) Fitting extension probability distribution of the DNA hairpin with 20 base pairs in the stem and the position of DNA mismatch in stem ranges from position (10) to (17). |
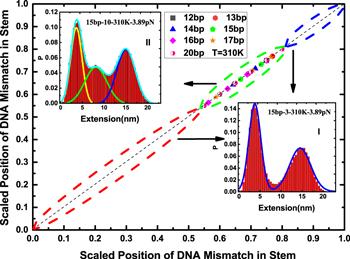
Figure 6. Phase diagram constructed in the phase space of the scaled position of DNA mismatch in the stem. The diagonal line in the phase diagram is divided into three segments, and the scaled position of DNA mismatch for the segment circled by a green dash line is in the range where the fitting of the extension histogram of the DNA hairpin is similar to the fitting in the inset (II) and has the folded state, intermediate state and unfolded state. As for those for the other sections circled by red and blue dash lines, they fell in the ranges where the extension histogram with two peaks could be compared with the one in the inset (I). The extension probability distribution in the insets (I) and (II) corresponds to the DNA hairpin with 15 base pairs in the stem and DNA mismatch is placed at positions (3) and (10), respectively. |
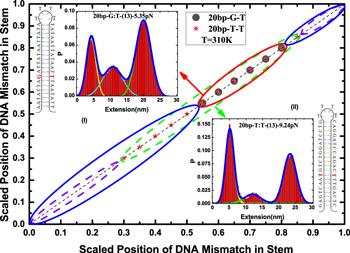
Figure 7. Phase diagram constructed in the phase space of the scaled position of DNA mismatch in the stem with 20 base pairs. The DNA hairpins with different sequences in the stem are separately indicated in the insets (I) and (II), where the DNA mismatch is placed at the position (13), and the corresponding extension distributions have folded, intermediate, and unfolded states. The diagonal line for different sequences in the phase diagram is divided into three segments, the segments circled by solid and dash lines separately correspond to the sequences in the insets (I) and (II).The scaled positions of DNA mismatch for the segments circled by a red solid and green dash lines separately fall in the ranges [0.55,0.85) and [0.3,0.90), where the extension distributions of the DNA hairpin have the folded, intermediate, and unfolded states. Their corresponding scaled position ranges are obviously extended by replacing the sequence in the inset (I) with the one in the inset (II). |