Residue-Specialized Membrane Poration Kinetics of Melittin and Its Variants: Insight from Mechanistic Landscapes *
|
Residue-Specialized Membrane Poration Kinetics of Melittin and Its Variants: Insight from Mechanistic Landscapes * |
| Zhi-Xiong Deng,Jing-Liang Li,Bing Yuan,Kai Yang |
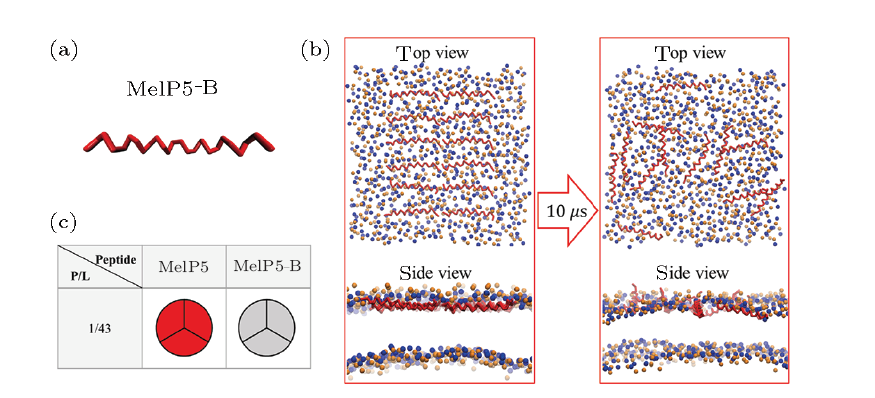
| Fig. S6 (Color online) (a) Conformational structure of MelP5-B which is the structure-variant of MelP5. (b) Interaction states between MelP5-B and the lipid bilayer. (c) Formation probability of membrane pore under the action of MelP5-B at $P/L$=1/43. For each parameter, three independent runs are performed to make statistics. Red: T-pore; grey: no pore. Herein, control simulations are carried out to confirm the important role of the kink structure of the peptide. A variant of MelP5, named MelP5-B, is built. MelP5-B has the same amino acid sequence as MelP5 while with a full $\alpha$-helical chain structure, but without the non $\alpha$-helical kink region (Fig. S6(a)). Energy calculations show that it is rather difficult for this peptide to form a "U" conformation (dashed line in |

|