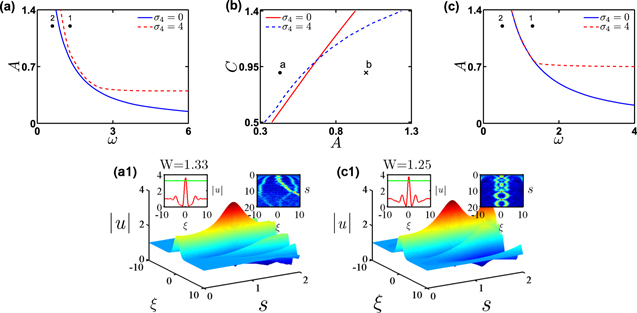
Figure 4. (a) The phase transition curves of the rogue wave for equation (7) as the function of the initial amplitude A and width w with σ4 = 0 and 4, when C = 1. Here, the dimensionless weak magnetic field w = 1 − 0.5ρ(ξ). (b) The phase transition curves of the rogue wave for equation (7) as the function of the initial amplitude A and the background height C with σ4 = 0 (red solid line) and σ4 = 4 (blue dotted line). Here, ω = 1.5, w is a random number. (c) The phase transition curves of the rogue wave for equation (7) as the function of the initial amplitude A and width w when taking C = 1. Here, the dimensionless weak magnetic field $w={{\rm{e}}}^{\left(-\tfrac{{\xi }^{4}}{{5}^{4}}\right)}$, σ4 = 0 and σ4 = 4, respectively. (a1) The evolution results of the initial incident pulse (8) with these parameters corresponding to the black point 1 in figure 4(a). Here, A = 1.2 and ω = 1.3. The FWHM of (a1) is W = 1.33. (c1) The evolution results of the initial incident pulse (8) by taking these parameters corresponding to the black point 1 in figure 4(c). Here, A = 1.2 and ω = 1.3. The FWHM of (c1) is W = 1.25.
|