Shape-changed propagations and interactions for the (3+1)-dimensional generalized Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation in fluids
|
Shape-changed propagations and interactions for the (3+1)-dimensional generalized Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation in fluids |
| Dan-Dan Zhang,Lei Wang,Lei Liu,Tai-Xing Liu,Wen-Rong Sun |
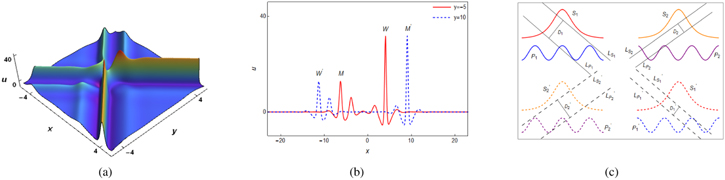
| Figure 14. (a) The inelastic collision between the W-shaped wave and M-shaped wave with $(\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma ,{a}_{1},{b}_{1},{c}_{1},{d}_{1},{g}_{1},{h}_{1}$, ${\lambda }_{1},{\beta }_{1},{\eta }_{1},{a}_{2},{b}_{2},{c}_{2},{d}_{2},{g}_{2},{h}_{2},{\lambda }_{3},{\beta }_{2},{\eta }_{2},z,t)$ = $\left(-1,-4,10,1,2,-1,-2,4,1,2,0,0,1,2,1,2,4,1,2,0,0,0,0\right)$. (b) The sectional views of (a). ‘W’ and ‘M’ represent the W-shaped wave and M-shaped wave, respectively. ‘W′’ and ‘M′’ represent the two waves after the collision respectively. (c) The schematic diagram of analysis of wave components. For the wave components constituting the M-shaped wave and W-shaped wave, due to the different phases, the superposition regions of the corresponding two wave components are different, which leads to obvious deformation of the two converted waves. |

|