The interference between a giant atom and an internal resonator
|
The interference between a giant atom and an internal resonator |
| Xiao-Pei Yang,Zhi-Kun Han,Wen Zheng,Dong Lan,Yang Yu |
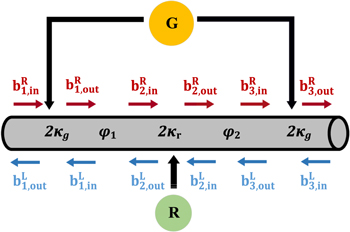
| Figure 1. Schematic diagram of our system. A giant atom (yellow) connects to the waveguide at the first and third points. A resonator (green) interacts with the waveguide at the second point. Their resonance frequencies are ωg and ωr, respectively. We assume the atom and resonator decay in both directions, ${\kappa }_{g}^{L}={\kappa }_{g}^{R}={\kappa }_{g}$ and ${\kappa }_{r}^{L}={\kappa }_{r}^{R}={\kappa }_{r}$, where L (left) and R (right) represent the decay direction. Then the total decay rate is 2κg and 2κr at the connection point. The fields through this system propagate in both directions. For example, ${b}_{1,\mathrm{in}}^{R}$ represents the incoming fields propagate to the right at the first connection point. φ1,2 is the phase shift between the nearest neighbor coupling point. |

|