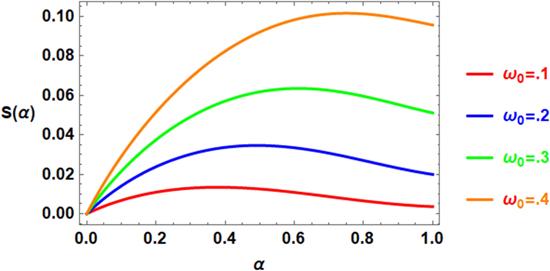
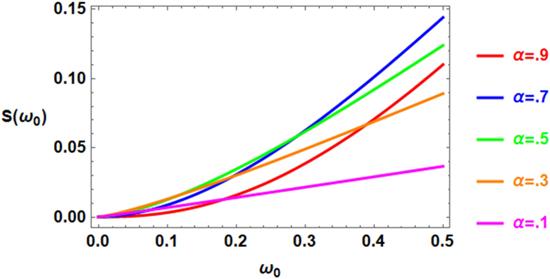
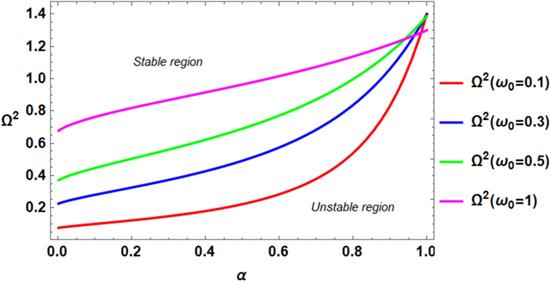
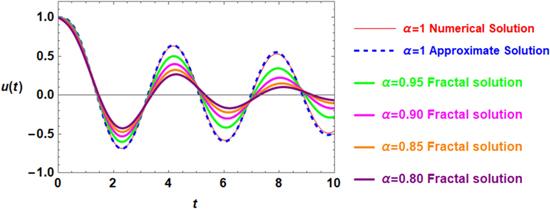
The fractal studying is an interesting idea that has distinctive applications in assorted areas, for instance, the physical phenomena of the hierarchical structure, diffusion, thermal conductivity within branched networks, meteorology, fluids flow resistance in micro-channels, ocean and atmosphere dynamics, nuclear and petroleum engineering, thermo elasticity, and materials design [
30–
38]. As a result of these important applications, the study of fractals was a fertile field for many scientists. Sheng
et al [
39] studied the fractal model of shale through a porous medium. For the fluid flow through a porous structure, another fractal model was investigated by Miao
et al [
40]. Further, by utilizing the mechanism of homotopy perturbation, He
et al [
41] evaluated an approximate solution for the Toda oscillator with fractal space. By employing the Hamilton principle, He
et al [
42.] also introduced a modern fractal modification to calculate a periodic solution for a fractal Duffing oscillator. During the steady state, an exact solution of a damped forced fractal oscillator was calculated in [
43]. Furthermore, by applying two-scale fractal derivatives, Feng [
44] obtained an analytic solution for Duffing oscillator in fractal space. Ain and He [
45] investigated the two-scale dimension to investigate some applications of fractal theory. Anjum and his colleagues [
46,
47] also introduced the two-scale fractal theory to investigate the mathematical models of tsunami waves and population, respectively. By using the two-scale fractal calculus, He and El-Dib [
48] analyzed the application of the fractal Shabat–Zhiber model. The fractal with two-scale and harmonic balance techniques was also applied by Lu and Chen [
49] to analyze a fractal Yao-Cheng oscillator. Further, Ain
et al [
50] used the two-scale fractal dimension to provide an in-depth study of the alcohol-drinking model that includes the fractional derivative. Zuo and Liu [
51] investigated a fractal rheological problem for SiC pastes using a fractal derivative. A two-scale technique was also used by Ain
et al [
52] and Yang
et al [
53] to investigate time-fractional heat transport and Varicella-Zoster virus models, respectively. Also, based on the two-scale fractal calculus, Huang
et al [
54]. developed a permeability fractal model for a porous medium. Moreover, Wang [
55] used He's frequency formula to solve another nonlinear fractal oscillator. In [
56,
57], the same author also proposed a clear frequency formulation to investigate the nonlinear oscillators with fractal space. In addition, Tian [
58] introduced another frequency formulation to deal with a system of fractal oscillators. Lately, in [
59], He
et al also employed fractals with two-scale derivatives to investigate a fractal vibration. In the field of microgravity space, Wang [
60] also used the Fourier series to propose a new technique for a class of fractal nonlinear oscillators that have discontinuities. For more analysis of the dynamical systems, El-Nabulsi
et al [
61] achieved a novel local derivative operator with fractal via both Hamiltonian and Lagrangian functions. On the other hand, there are a lot of effective contributions to ‘analytical approximation’ and ‘fractional/fractal’ modeling in the literature. By employing natural transforms and fractional calculus, respectively, Nadeem
et al [
62] and Elgazery [
63] proposed numerical and analytical solutions to the fractional nonlinear Newell-Whitehead-Siegel model. A numerical solution of a reaction-diffusion/advection model with time fraction derivatives in porous media was also introduced by Pandey
et al [
64]. El-Dib
et al [
65] also provided an analytical solution for the Klein–Gordon model with time fraction derivatives. For more recent and significant contributions, see [
28,
66–
68].